Researchers formulate new yogurts with high protein content and higher satiating capacity

Researchers of the Universitat Politècnica de València and the Instituto de Agroquímica y Tecnología de Alimentos (IATA) of the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) have obtained in the laboratory a new yogurt with high protein content and higher satiating capacity. The work has been published in the journal Food Research International and it opens up an alternative in the design of new nutritional control strategies.
The CSIC research doctor and project coordinator, Susana Fiszman, explains that "in the market, there is a real necessity to formulate food that helps to control the appetite; this is why we suggested formulating a yogurt with satiating capacity as an interesting strategy, and it was successfully developed." Isabel Hernando, researcher at the Group of Microstructure and Food Chemistry of the Universitat Politècnica de València, says that protein is the most effective macronutrient in obtaining a satiating effect, "that is what makes the formulation of dairy products with higher protein content able to help moderate food consumption."
In their study, the researchers of the Universitat Politècnica de València and the IATA (CSIC) assessed up to six different types of yogurt: they added powdered skimmed milk to one of them, they incorporated a buttermilk protein to the second and the third one was the "control yogurt," that is, without added protein. In order to obtain the other three, they added 2% starch to each of the above formulae, aiming to improve the perception of a creamy texture.
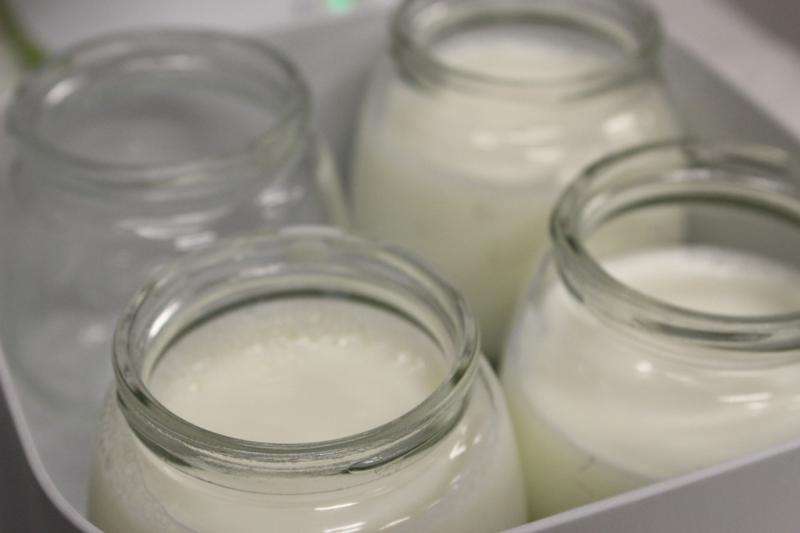

In order to determine their satiating capacity, they ran sensory tests, in which more than a hundred consumers took part. Among all of the products, the formula with powdered skimmed milk and starch was the one that caused most expectations about the satiating capacity.
"Moreover, the addition of starch in the control sample significantly raised the perception of its satiating capacity, so its use to reinforce this capacity could be a useful tool in this kind of dairy products," says Isabel Hernando.
Satiety sensation and new products
The researchers also analysed how the consumer's sensory perception has an influence on the satiating capacity. "Powdered milk and starch yogurt was defined as the densest, the most compact and the creamiest, attributes that led to a greater expectation of satiating capacity in the consumers," explains Isabel Hernando.
In addition, they studied how the addition of proteins and starch affects the microstructural and rheological properties of the products, as well as their thickness and consistency, the oral transit and, as a consequence, the consumer's final acceptance.
The researchers of the IATA (CSIC) and the Universitat Politècnica de València are continuing their work on the design of new strategies of addition of satiating ingredients to daily food. Among others, they are studying new formulae for cheesecake.
More information: "Yogurts with an increased protein content and physically modified starch: rheological, structural, oral digestion and sensory properties related to enhanced satiating capacity." Food Research International. Volume 70. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodres.2015.01.024
Provided by Asociacion RUVID