NASA image: Seasonal flows in the central mountains of Hale Crater
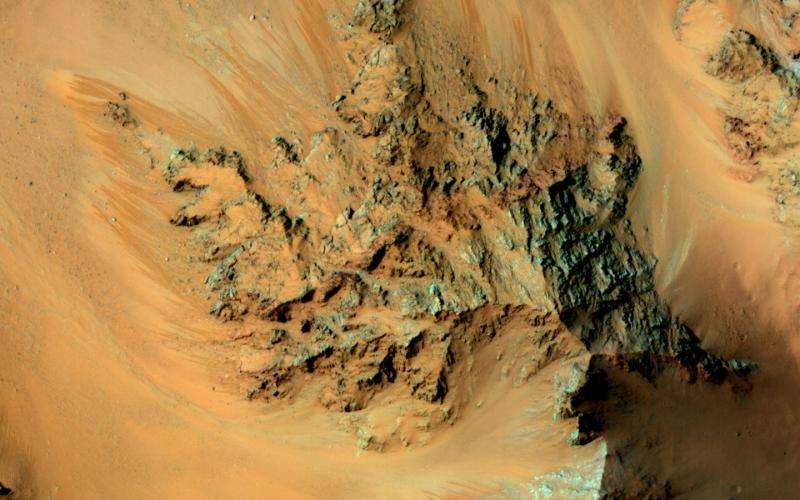

Recurring slope lineae (RSL) are active flows on warm Martian slopes that might be caused by seeping water. One of the most active sites known on Mars is in the central peaks (uplifted mountains of deep bedrock) of Hale Crater.
This image shows RSL extending downhill from bedrock cliffs, mostly towards the northwest (upper left). This image was acquired in middle summer when RSL are most active in the southern mid latitudes.
The RSL in Hale have an unusually "reddish" color compared to most RSL, perhaps due to oxidized iron compounds, like rust. Since HiRISE color is shifted to infra-red wavelengths, they are actually especially bright the near-infrared just beyond the range of human vision.
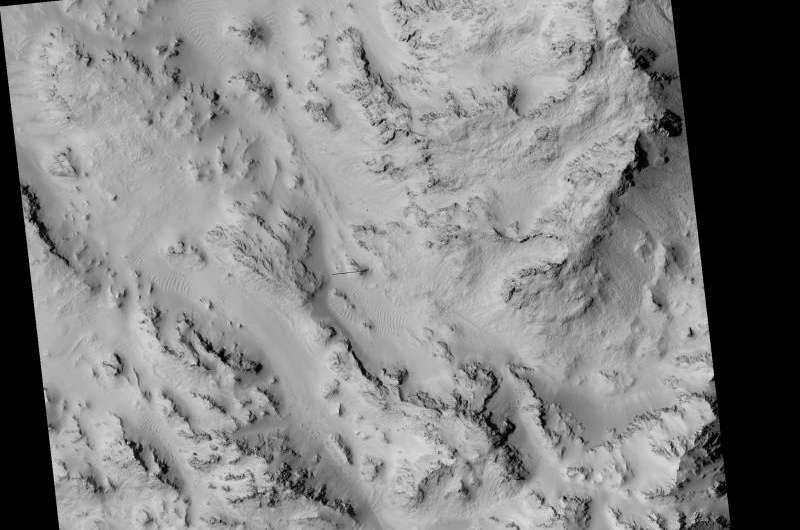
The Hale RSL are also unusual because they began activity much earlier than most RSL sites in the middle southern latitudes, and were well-developed in the early spring (see ESP_038073_1440). If seeping water causes RSL in Hale crater, it must be rich in salts to lower its freezing point significantly below the freezing point of pure water.

Provided by Jet Propulsion Laboratory