Against-the-clock rehearsal for Station immunology test

Simply getting anything into space is tough, but doing so against a strict deadline can be really stressful. Researchers in an ESA laboratory nervously checked the clock as they extracted immune cells – beginning a full dress rehearsal to prepare a time-critical experiment for launch.
An international team led by a NASA astronaut gathered at ESA's Life and Physical Sciences and Life Support Laboratory at ESTEC technical centre in Noordwijk, the Netherlands, earlier this month. There they rehearsed preparing their payload for flight to the International Space Station by Dragon capsule this November.
The experiment involves activating T-cells – central to the human immune response – in microgravity to test how their behaviour changes. Previous research has shown that suppressed immune systems of astronauts in orbit come about largely due to weightlessness.
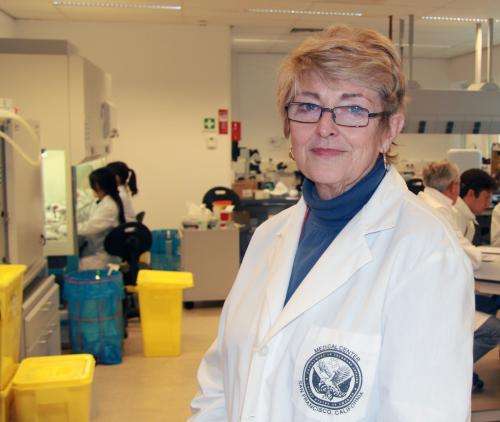
"We're trying to pinpoint the very small molecules that regulate the immune system – with microgravity experimentation serving to reveal new regulatory pathways," explains astronaut and molecular biologist Millie Hughes-Fulford, veteran of 1991's STS-40, the first Shuttle mission devoted to medical science.

"With autoimmune diseases like arthritis you're looking for ways of turning the immune response down while with astronauts or older people down on Earth you really want to turn it up because it isn't working as well.
"This is why we're doing this experiment on healthy cells in spaceflight – to find the pathways that are affected very early and then we're going to study the immune system of older people and see if the same mechanisms are at work."
The challenge is that T-cells must be extracted fresh from human blood – and survive only 120 hours once outside it.
Within that time they have to be isolated, prepared for their spaceflight inside 'experiment units' which must then be checked for integrity, passed to SpaceX technicians for loading aboard Dragon, undergo the two-day launch and rendezvous with the Space Station, then be unloaded and placed inside ESA's Kubik incubator within Europe's Columbus module where the actual experiment will take place.

Once safely inside the 37°C incubator – with some placed inside an internal centrifuge to serve as normal-gravity controls – the T-cells will be activated using synthetic antigens to provoke an immune response. The cells will then have their expressed RNA preserved for subsequent analysis.
The payload is due to be downloaded back to Earth by the returning Dragon at the end of this year.
Principal investigator Dr Hughes-Fulford and her research team from the University of California San Francisco joined with the experiment's hardware designers at Kayser Italia and ESA's Swiss ISS User Support Operations Centre for the rehearsal, covering all experimental milestones other than launch.
"The process can be stressful but this dress rehearsal has made us prepare for it, making us more ready for the actual flight," adds Dr Hughes-Fulford.
While officially a US experiment, ESA is providing support through a barter agreement. The experiment will be prepared for actual flight adjacent to the launch site at NASA's Kennedy Space Center.
For Dr Hughes-Fulford this experiment is the latest of many orbital experiments: "During my Shuttle flight we oversaw 26 separate experiments covering all areas of medical science. In my subsequent research career I've focused on the immune system as one of the most important areas to be affected during spaceflight.
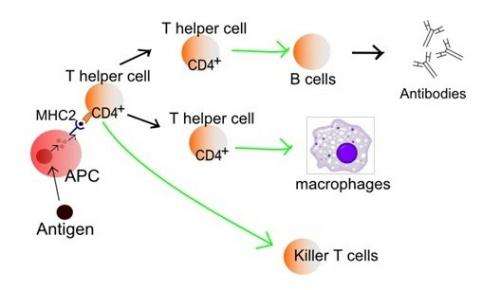
"We also have a lot of people on the ground with auto-immune diseases, or older people dying of infection because their immune system is compromised, so it's a very important field of study – not just for astronauts going to Mars but actually for everybody."
"ESTEC's Life and Physical Sciences and Life Support Laboratory regularly supports preparation for similar biological experiments," adds ESA's Jutta Krause.
"Our Lab is equipped for a wide variety of activities including technology developments and hardware testing up to full-scale dress rehearsals like this."
Provided by European Space Agency