NRL Nike Laser focuses on nuclear fusion
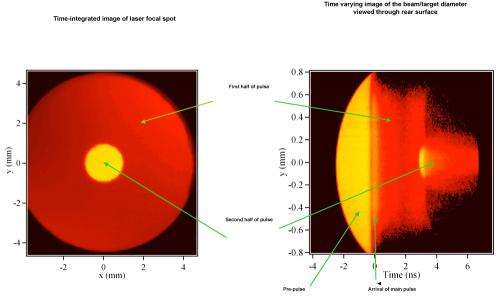
Researchers at the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory have successfully demonstrated pulse tailoring, producing a time varying focal spot size known as 'focal zooming' on the world's largest operating krypton fluoride (KrF) gas laser.
The Nike laser is a two to three kilojoule (kJ) KrF system that incorporates beam smoothing by induced spatial incoherence (ISI) to achieve one percent non-uniformity in single beams and 0.16 percent non-uniformity for 44 overlapped target beams. The facility routinely conducts experiments in support of inertial confinement fusion, laser-matter interactions and high energy density physics.
"The development of an energy production system that utilizes thermonuclear fusion is an ongoing process of important incremental steps," said David Kehne, research scientist, NRL Plasma Physics Division. "As such, the use of focal zooming in an inertial fusion energy system is expected to reduce the required laser size by 30 percent, resulting in higher efficiency and lower construction and operating costs."
In the direct-drive inertial confinement fusion (ICF) concept, numerous laser beams are used to implode and compress a pea-sized pellet of deuterium-tritium (D-T) to extreme density and temperature, causing the atoms to fuse, resulting in the release of excess energy.
In an ICF implosion, a progressively diminishing portion of the beams will engage the shrinking pellet if the focal spot diameter of the laser remains unchanged. For optimal coupling, it becomes desirable to decrease the laser focal spot size to match the reduction in the pellet's diameter, minimizing wasted energy.
"Matching the focal spot size to the pellet throughout the implosion process maximizes the on-target laser energy," Kehne said. "This experiment validates the engineering of focal zooming in KrF lasers to track the size of an imploding pellet in inertial confinement fusion."
With single-step focal zooming implemented, the Nike laser provides independent control of pulse shape, time of arrival, and focal diameter allowing greater flexibility in the profiles and pulse shapes that can be produced. The flexibility in pulse shaping provides promising uses in both future experiments and laser diagnosis.
Provided by Naval Research Laboratory