Nanoscale edge variations observed with record-breaking resolution in magnetic nanodevices
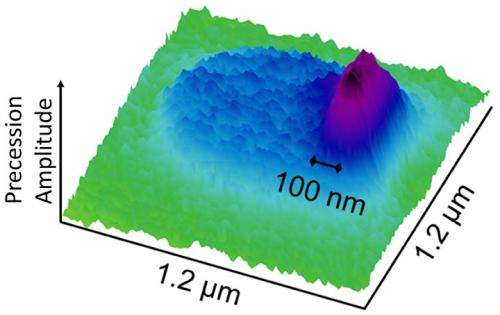
(Phys.org) —A team of researchers from the Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, the University of Maryland, and the NIST Center for Nanoscale Science and Technology have measured large variations in the magnetic properties along the edge of a thin film 500 nm-diameter disk. This work represents a significant development in the measurement of magnetic thin film edge properties, which are especially important for nanodevices, such as magnetic memory cells, where the edge to area ratio is large.
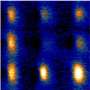
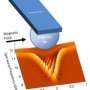
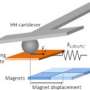
The researchers' technique, called ferromagnetic resonance force microscopy, detects magnetic resonance in a sample through changes in the magnetic force between the sample and a magnetic cantilever tip. The technique uses an external field from a nearby microwave antenna to excite a magnetic resonance that causes the sample's magnetization to precess, wobbling like a top, billions of times per second. This precession leads to a small decrease in the time-averaged magnetization that can be detected as a change in the magnetic force on the cantilever. With an external field applied in the plane of the film, modeling predicts that an "edge mode" forms in which the precession is localized to within 30 nm of the edge. The recent measurements profiled that edge mode with a record 100 nm resolution. By rotating the applied field direction, the location of the edge mode is then moved along the circumference of the disk, with changes in the magnetic resonance mapping out variations in magnetic properties along the edge.
The researchers believe that continued development of ferromagnetic resonance force microscopy methods will enable measurements of individual magnetic nanodevices, providing important new information about the properties of these devices and their potential defects.
More information: Guo, F., Belova, L. and McMichael, R. Physical Review Letters 110, 017601 (2013). link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.017601
Journal information: Physical Review Letters
Provided by National Institute of Standards and Technology