10-year study reveals incredible level of accuracy to estimate intrinsic magnetic properties of two subatomic particles
The electron is found in every atom and plays a key role in almost every chemical reaction. So, a complete understanding of its physical properties is vital. Researchers from the RIKEN Nishina Center for Accelerator-Based Science, together with their colleagues from Nagoya University, Japan, and Cornell University in the US, have completed the most precise calculations of the magnetic properties of the electron and a similar, heavier particle known as a muon. These results provide a stringent test of physicists' understanding of the subatomic world.
The most accurate theory for describing elementary particles that scientists have yet created is called the 'standard model'. This model divides fundamental particles into three broad categories: quarks, which make up most of the mass around us; gauge bosons, which are responsible for forces that hold this matter together; and leptons, which include both the electron and the muon. Leptons are characterized by their mass, their electric charge and their magnetic moment—a measure of the particle's intrinsic magnetic properties.
British scientist Paul Dirac predicted that the magnetic moment of leptons should be exactly two. However, scientists have known for a long time that the actual value varies very slightly from this perfect number because of quantum effects. RIKEN researcher Makiko Nio and her colleagues have performed state-of-the-art computational analysis of this anomalous magnetic moment of both the electron and the muon.
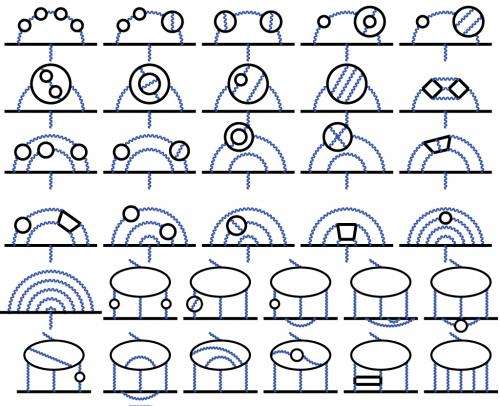
Particle physicists describe the behavior of elementary particles using pictorial representations known as Feynman diagrams. Nio and her co-workers included in their calculations all of the 12,672 Feynman diagrams relevant to the anomalous magnetic moment of the electron, far more than any previous work. "To handle these enormous and tedious calculations, we developed an automated code-generating system, and carried out computations using supercomputers at RIKEN for almost 10 years," says Nio. They were thus able to provide a value for the electron anomalous magnetic moment that was accurate to 0.24 parts per billion. "With these results we have also obtained the world-best value of the fine-structure constant, which determines the strength of electromagnetic interactions," she says.
The researchers also performed similar calculations to provide a more accurate estimation of the muon anomalous magnetic moment. Their improved value confirms the previous result which does not fully agree with that expected from the standard model. The researchers believe that this discrepancy between the measurement and theoretical prediction may lead to new physics beyond the standard model of elementary particles.
More information: Aoyama, T., Hayakawa, M., Kinoshita, T. & Nio, M. Tenth-order QED contribution to the electron g-2 and an improved value of the fine structure constant. Physical Review Letters 109, 111807 (2012). prl.aps.org/abstract/PRL/v109/i11/e111807
Aoyama, T., Hayakawa, M., Kinoshita, T. & Nio, M. Complete tenth-order QED contribution to the muon g-2. Physical Review Letters 109, 111808 (2012). prl.aps.org/abstract/PRL/v109/i11/e111808
Journal information: Physical Review Letters
Provided by RIKEN