Researchers seek way to make solar cells ultra-thin, flexible

Researchers at The University of Texas at Dallas are developing nanotechnology that could lead to a new platform for solar cells, one that could drive the development of lighter, flexible and more versatile solar-powered technology than is currently available.
The National Science Foundation recently awarded a $390,000 grant to Dr. Anton Malko and Dr. Yuri Gartstein, both in the Department of Physics, and Dr. Yves Chabal in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering to further explore their research on the feasibility of ultrathin-film photovoltaic devices, which convert light from the sun into electric power.
"Traditional silicon solar cells that are commercially available are made from silicon that is a couple of hundred microns thick," Malko said. "Our goal is to reduce that by a hundred times, down to about one micron thick, while at the same time maintaining efficiency."
A micron, or micrometer, is a unit of measurement, equal to one millionth of a meter. For comparison, the diameter of a human hair is about 100 microns, and a U.S. dime coin is about 1,250 microns thick.
While the scale of the research objects is tiny, their impact could be substantial.
"Solar cells that are 100 microns thick are rigid and fragile," Malko said. "At the thickness we are investigating, devices would not only be lighter, but they also become flexible. There is a large market and application niche for flexible solar cells, such as on clothing or backpacks for hikers, or in situations where you need portable sources to power electronics."
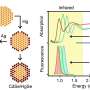
The UT Dallas approach to building solar cells involves the use of nanosized crystal particles called quantum dots, which absorb light much better than silicon. The energy they absorb is then transferred into silicon and converted into an electric signal.
The researchers construct their experimental photovoltaic structures layer by layer, starting with an ultrathin layer of silicon, a so-called nanomembrane about one-tenth of a micron thick. On top of that, with the aid of special molecular "linkers," layers of accurately positioned quantum dots are added.
"This is not yet an engineering project, it's a research project," Gartstein said. "We believe we are asking interesting scientific questions and researching concepts that might eventually lead to devices."
Initial findings from the research were published recently in the journal ACS Nano.
"The key point of our research is to characterize the way energy is transferred from the quantum dots through the layers to the silicon, as well as to determine how we might exploit those properties and optimize the arrangement of the quantum dots, the thickness of the layers and other aspects of the structure," Malko said.
The cross-disciplinary research involves not only proficiency in experimental and theoretical physics, which Malko and Gartstein provide. Materials science and nanotechnology expertise is also crucial. A key member of the team is Dr. Oliver Seitz, a postdoctoral researcher in Chabal's laboratory, who carried out the delicate and precisely controlled process of actually building the test structures.
"This project, conceived and initiated by Anton Malko, has been exciting at all stages of research," said Chabal, holder of the Texas Instruments Distinguished University Chair in Nanoelectronics. "It has engaged my group into an exciting application relying on the chemical control of surfaces we have been developing."
Gartstein added: "This is one of those cases where the word 'synergy' truly applies. As a theorist, I can come up with some ideas and do some calculations, but I cannot build these things. In materials science, Dr. Seitz actually implements our joint ideas to make the physical samples. Then in Dr. Malko's lab, ultrafast laser spectroscopy is used to physically measure the relevant processes and properties. Hue Minh Nguyen, a physics graduate student, contributed tremendously to this effort.
"It's been a great pleasure to work together in this atmosphere of a true collaboration," he said.
Journal information: ACS Nano
Provided by University of Texas at Dallas