Breaking boundaries in tiny labs: New technology using sound waves has implications for nanoparticle manipulation
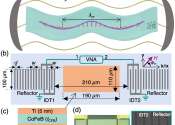
Acoustofluidics elegantly merges acoustics with fluid mechanics, enabling precise manipulation of fluids and particles on both micro and nanoscales. This interdisciplinary field plays a crucial role in biomedicine, tissue ...