TRMM satellite tallies Hurricane Odile's heavy rainfall
During the week of Sept. 15, Hurricane Odile and its weakened remnants produced heavy rainfall that caused dangerous flooding over Mexico's Baja California peninsula and southwestern United States. NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite gathers data on rainfall that was used to create a map that showed estimated totals that in one case neared almost three feet!
Some of Odile's may have been welcomed in the U.S. Southwest where some areas have been experiencing extreme to exceptional drought conditions, but some was extreme and led to flooding.
TRMM was launched in November 1997 with the primary mission of measuring rainfall in the Tropics using a combination of passive microwave and active radar sensors. It is a joint mission between NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency.
A rainfall analysis was created using real-time TRMM Multi-Satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) data produced at the NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Those data are used to monitor rainfall over the global Tropics.
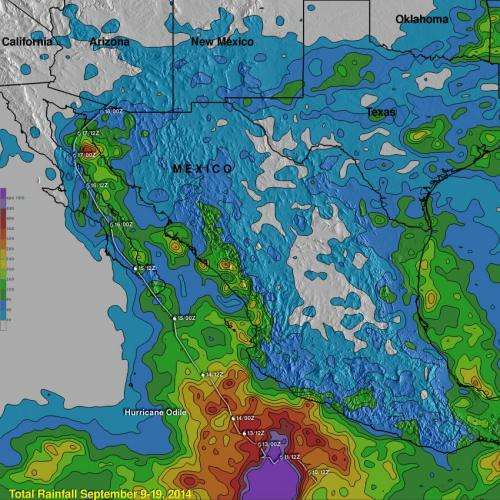
TMPA rainfall totals from September 9 through 19, 2014 were gathered during the period when Hurricane Odile formed over the eastern Pacific Ocean southwest of Mexico, hit Baja California and when the dissipating tropical cyclone was spreading rainfall over the southwestern United States. The heaviest rainfall during this period was found in the ocean off southwestern Mexico where Odile and other tropical cyclones have recently formed. In that area, rainfall totals reached up to 840 mm (33 inches) , almost three feet!
Rainfall along Mexico's Baja California Peninsula were over a foot. TRMM data showed rainfall totals above 320 mm (12.5 inches) there. The TRMM analysis showed that in southwestern United States Odile's remnants produced the highest rainfall totals of over 160 mm (6.3 inches) in northwestern Texas.
Provided by NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center