Engineers unveil two-way wireless breakthrough
(Phys.org) -- Groundbreaking two-way wireless technology resulting in vastly superior voice and data services has been developed by a University of Waterloo engineering research team led by Amir K. Khandani, the Canada Research Chair in Wireless Systems.
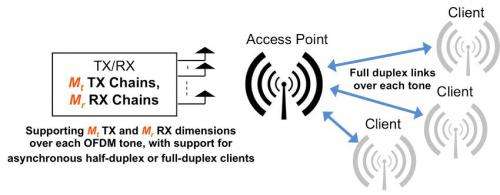
The new technology enables wireless signals to be sent and received at the same time on a single radio channel frequency. "This means wireless companies can increase the bandwidth of voice and data services by at least a factor of two by sending and receiving at the same time, and potentially by a much higher factor through better adaptive transmission and user management in existing networks," said Khandani, a Waterloo electrical and computer engineering professor.
Current wireless systems suffer from shortcomings similar to old walkie-talkies that don’t allow users to talk and listen on the same frequency at the same time. That's because the strength of the transmission overwhelms any incoming signal on the same frequency.
“Wireless is in desperate need of a breakthrough, and two-way comes at the right time," Khandani added. "The cost in hardware and signal processing complexities and antenna size is very low and virtually the same as current one-way systems. Two-way wireless systems will also have a profound impact on wireless networks in terms of quality of service and efficiency.”
The wireless advancement also opens the possibility to have ultra-secure transmission. “This can be done in ways that are much superior to current encryption techniques that are not truly secret, just hard to guess," said Khandani.
His research group is well known for introducing breakthrough ideas in wireless industry. In 2006, it came up with the idea of Interference Alignment, which radically changed the mindset about interference management, and it is now a mainstream in academic and industry research. Khandani predicts two-way wireless will reshape the future of the wireless industry, which is under overwhelming pressure for higher data rates.
The Waterloo Engineering research breakthrough is based on technology patented by Khandani in 2006 and issued in 2010, with many more innovations since then.
The video clip introduces many new applications for two-way technology such as methods for interference management, security enhancement, and a unique approach to wireless connectivity called media-based, which is created by embedding data in transmission media rather than in the transmitted RF signal. Media-based approach offers significant benefits compared to traditional MIMO systems even with a smaller number of antennas.
Next steps requires industry involvement by including two-way in forthcoming standards to enable wide spread implementation.
More information: www.cst.uwaterloo.ca/2way/
Provided by University of Waterloo