Research explains success of extremist politicians
Today's longer campaign cycles, filled with numerous televised debates and constant news reporting and social media coverage, are causing the rise of extremist politicians, according to a new study from the University of Miami School of Business Administration, just published in the American Economic Journal: Economics. The research, which utilized game theory, finds that longer campaigns, which offer voters more information on the candidates via 24-hour news coverage and social media, turn voters' attention more toward a candidate's character - such as trustworthiness and how he or she delivers speeches and exchanges debate barbs - and away from his or her stance on policy. With this in mind, politicians now have less incentive to moderate their messages, a tactic often used in order to bring swing voters to ballot boxes as they tend to vote for more moderate candidates.
"Our research shows real impact associated with longer, more informative campaigns, and perhaps a reason why we are seeing candidates like Donald Trump and Bernie Sanders doing so well within their parties this late in the game," said Raphael Boleslavsky, assistant professor of economics at the University of Miami School of Business Administration, who conducted the study along with Christopher Cotton of Queens University. "Candidates base their platforms on how to capture the majority of voters relative to their opponent so our research suggests that extremism is likely something we will see more as campaign cycles continue to get longer and longer."
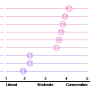
According to the researchers, a shorter campaign cycle with less time for media saturation might allow voters to experience a greater balance of a candidate's policy positions and character. This would lead to better-informed voters because of more attention on policy issues. Further, increasing the number of debates in an election cycle, according to the study, decreases the incentive for politicians to run on moderate platforms.
Methodology:
For this study, the authors developed a mathematical model of an election in which parties nominate candidates with policy preferences ahead of a campaign that produces information about their overall characteristics independent of policy. The mathematical model used the tools of game theory, which allowed researchers to describe strategic situations and understand strategic incentives in a mathematically rigorous way. They then solved the equations generated by the model, resulting in a robust prediction about the level of political extremism that political parties select, and how this level of extremism changes with the length of the political campaign.
"Over the next eight months our country will likely judge our next president, not only on his or her policy proposals, but also on his or her television performance in debates and speeches, and our perception of his or her character. These other dimensions may be relevant to the candidate's capability to lead, but unfortunately, there is a link between our ability to learn about these dimensions and candidates ideological extremism. Because we started thinking about our next leader so early, the moderate policies many voters want may not be on the table."
More information: Raphael Boleslavsky et al. Information and Extremism in Elections , American Economic Journal: Microeconomics (2015). DOI: 10.1257/mic.20130006
Provided by University of Miami