Huge sunspots and their magnetic structure observed by Hinode
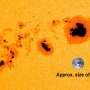
In the latter half of October, huge sunspots were observed on the surface of the Sun. These sunspots appeared at the east limb of the Sun on Oct. 16, and moved to the west as the Sun rotated. They rotated out of view after Oct. 30. On Oct. 26, the total area of these sunspots became almost 66 times larger than the Earth's cross section. This was the largest sunspot area in this solar cycle, and the largest observed in the last 24 years (since Nov. 18, 1990). In the middle of November, these sunspots appeared again at the east limb, as the Sun's rotation brought them back into view.
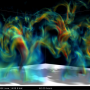
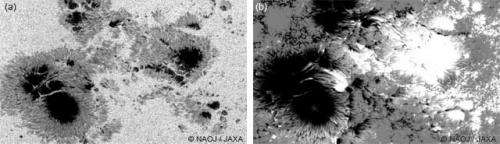
Fig.1 and Fig.2 show the sunspots captured by the solar observing satellite "Hinode" on Oct. 24 and Nov. 15, respectively. In these figures, image (a) is a white light image, and image (b) is the magnetic field map (white = positive (N) pole, black = negative (S) pole).
Sunspots look darker because their temperature is lower than the surrounding. Strong magnetic fields in the sunspots lower the temperature, because the magnetic fields obstruct the convection that transports the heat generated in the center of the Sun to the solar surface. Strong magnetic fields sometimes cause solar "flares", huge explosions which occur in the solar atmosphere. Therefore, one of the reasons why "Hinode" accurately measures the magnetic fields on the solar surface is to understand the mechanism of solar flares.
How do solar flares influence the Earth? Sometimes when flares occur, high-energy charged particles reach the Earth and magnetic storms occur. In October, the terrestrial environment was not disturbed much, although many flares occured on the solar surface. The reason is under investigation; one possibility is that the magnetic field in the solar upper atmosphere was so strong that it suppressed the eruption of charged particles. In November, even if there are fewer large flares than in October, there could be flares which greatly influence the Earth. We should carefully watch the evolution of the sunspots.
-
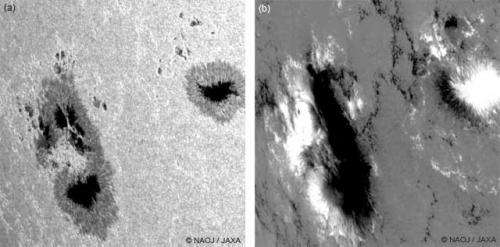
Figure 2: (a) White light image of the sunspots and (b) Magnetic field map of the sunspots on Nov. 15, 2014 taken by “Hinode”. (Field of view) w: aprox.120,000 km × h: aprox.120,000 km -
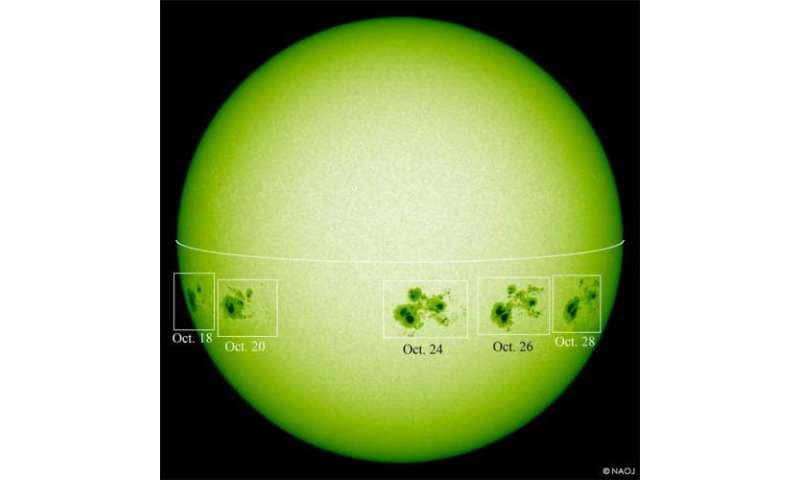

Figure 3: White light images of the sunspots taken by the Solar Flare Telescope of the Solar Observatory/NAOJ from Oct. 18 to 28, 2014. (Only the huge sunspots are superimposed.)