Super strong antimicrobial coatings for medicine, defense
One of the world' strongest materials meets one of Nature's most powerful germ killers in a new research project that produced incredibly tough anti-bacterial surfaces with multiple applications in home appliances, medicine, aerospace, and national defense. A report on this long-awaited genre of stronger disinfectant surfaces is scheduled for the July 9 issue of ACS' Nano Letters.
In the study, Virginia A. Davis and Aleksandr Simonian and colleagues point out that concern over the role of contaminated surfaces in the spread of infections has sparked a search for better antimicrobial coatings.
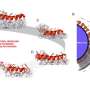
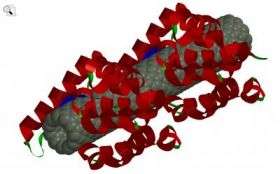
Scientists want to harness a powerful natural enzyme called lysozyme in that quest. However, they have not found a material strong enough to hold the enzyme in the desired fashion for long periods.
Their solution involved the first successful merging of lysozyme with single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNTs). Only 1/50th the width of a human hair, SWNTs have exceptional strength and hold lysozyme in place, while other coatings lose their antimicrobial activity over time.
"The results of this research demonstrate the significant possibilities for the molecular design of hybrid structural materials from SWNTs and natural biopolymers," the report states. "Such robust, antimicrobial materials have significant promise in applications including medicine, aerospace engineering, public transportation, home appliances and sporting goods."
Source: ACS