Catching a star: A new species of starfish discovered in Japan
Researchers in Japan have discovered a new species of starfish. The discovery came about thanks to collaborative work among researchers, fishers, and aquarium and museum staff.

Researchers in Japan have discovered a new species of starfish. The discovery came about thanks to collaborative work among researchers, fishers, and aquarium and museum staff.
Plants & Animals
Aug 5, 2024
0
18

Opponents of deep sea mining suffered a serious setback Friday when they failed to take a first step toward an international moratorium on the controversial practice.
Environment
Aug 3, 2024
1
27
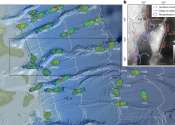
A new study has revealed that changes in the ocean floor impact currents, giving new insight into the deep-sea pathways of nutrients and pollutants.
Earth Sciences
Jul 31, 2024
0
12

An international team of researchers, including a Northwestern University chemist, has discovered that metallic minerals on the deep-ocean floor produce oxygen—13,000 feet below the surface.
Earth Sciences
Jul 22, 2024
1
350

Methane, a strong greenhouse gas that naturally escapes from the bottom of the North Sea, is affected by the pressure of high or low tide. Methane emissions from the sea floor can be just easily three times as much or as ...
Environment
Jul 12, 2024
0
29

Transparent sea cucumbers, bowl-shaped sponges, and pink sea pigs are some of the fascinating animals discovered during a deep-sea expedition to the Pacific Ocean.
Plants & Animals
Jun 5, 2024
0
260

Members of the vertebrate group including anglerfish are unique in possessing a characteristic known as sexual parasitism, in which males temporarily attach or permanently fuse with females to mate. Now, researchers reporting ...
Evolution
May 23, 2024
0
68

Analysis of mooring observations and hydrographic data suggest the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation deep water limb in the North Atlantic has weakened. Two decades of continual observations provide a greater understanding ...
Earth Sciences
Apr 19, 2024
0
305

"The science we need for the ocean we want"—this is the tagline for the UN Ocean Decade (2021-2030), which has just held its first conference in Barcelona, Spain. Marine scientists from around the world, including me, gathered ...
Environment
Apr 15, 2024
0
43

New research from CSIRO, Australia's national science agency, and the University of Toronto in Canada, estimates up to 11 million metric tons of plastic pollution is sitting on the ocean floor. The article, "Plastics in the ...
Environment
Apr 5, 2024
1
104
The seabed (also known as the seafloor, sea floor, or ocean floor) is the bottom of the ocean. At the bottom of the continental slope is the continental rise, which is caused by sediment cascading down the continental slope. The seabed has been explored by submersibles such as Alvin and, to some extent, scuba divers with special apparatuses. The process that continually adds new material to the ocean floor is seafloor spreading and the continental slope.
This text uses material from Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY-SA