New high-throughput screening technique makes probing puzzling proteins possible
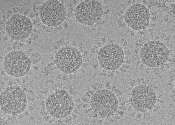
Understanding the tens of thousands of proteins that compose the human proteome has emerged as a key challenge of this century, and research efforts to date have already enabled major advances in drug discovery and understanding ...