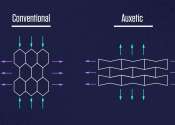
Nanoconfined materials developed for efficient fluoride removal from water
A research team led by Prof. Kong Lingtao from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed an innovative material for the efficient removal of fluoride ions from water. This newly-developed ...