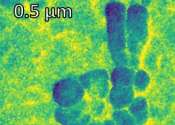
IRIS beamline at BESSY II gets a new nanospectroscopy end station
The IRIS infrared beamline at the BESSY II storage ring now offers a fourth option for characterizing materials, cells and even molecules on different length scales. The team has extended the IRIS beamline with an end station ...