Electrons in the water
It's a popular tradition to throw coins into fountains in the hopes of having wishes granted. But what would happen if you could "throw" electrons into the water instead? That is, what happens shortly after an electron is ...

It's a popular tradition to throw coins into fountains in the hopes of having wishes granted. But what would happen if you could "throw" electrons into the water instead? That is, what happens shortly after an electron is ...
Materials Science
Jan 22, 2018
0
83
Rydberg atoms are highly sensitive atoms, as one electron is only loosely bound. Compared to 'normal' atoms which are one tenth of a nanometer in size those giant atoms are ~100 nanometers large. Due to their sensitivity ...
Optics & Photonics
Jan 14, 2010
8
0

Semiconductor moiré superlattices are fascinating material structures that have been found to be promising for studying correlated electron states and quantum physics phenomena. These structures, made up of artificial atom ...

(Phys.org)—Cornell researchers have resolved a longstanding theoretical debate about the electronic structure of iron-based superconductors by directly observing it at the atomic scale. The work is reported in the Feb. ...
Superconductivity
Feb 21, 2013
70
0

Extension of cable-based telecommunication networks requires high investments in both conurbations and rural areas. Broadband data transmission via radio relay links might help to cross rivers, motorways or nature protection ...
Optics & Photonics
Oct 14, 2013
1
0
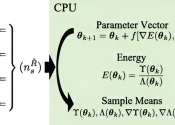
U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) scientists have published the Cascaded Variational Quantum Eigensolver (CVQE) algorithm in a recent Physical Review Research article. The algorithm is expected to become a powerful tool ...
Quantum Physics
Mar 25, 2024
0
527
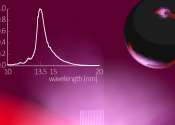
Extreme ultraviolet light (EUV light) does not naturally occur on Earth, but it can be produced. In nanolithography machines, EUV light is generated using an immensely hot tin plasma. Researchers at ARCNL, in close collaboration ...
Plasma Physics
May 11, 2020
1
78

During their research for a new paper on quantum computing, HongWen Jiang, a UCLA professor of physics, and Joshua Schoenfield, a graduate student in his lab, ran into a recurring problem: They were so excited about the progress ...
Quantum Physics
Jul 7, 2017
1
572

(PhysOrg.com) -- Graphene, a single-atom-thick sheet of carbon, holds remarkable promise for future nanoelectronics applications. Whether graphene actually cuts it in industry, however, depends upon how graphene is cut, say ...
Nanophysics
Feb 15, 2009
3
0

Bay, fjord, cove, armchair and zigzag—chemists use terms such as these to describe the shapes taken by the edges of nanographene. Graphene consists of a single-layered carbon structure in which each carbon atom is surrounded ...
Nanomaterials
Jan 30, 2019
0
436