Why does my hair turn green from the swimming pool?
If you are a blonde like me and enjoy laps in a swimming pool, you may have noticed your hair acquires a green tint after frequent swims in chlorinated water.

If you are a blonde like me and enjoy laps in a swimming pool, you may have noticed your hair acquires a green tint after frequent swims in chlorinated water.
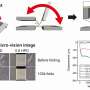
The rapid advancements in flexible electronic technology have led to the emergence of innovative devices such as foldable displays, wearables, e-skin, and medical devices. These breakthroughs have created a growing demand ...
Electronic devices that can be attached to the skin or even implanted in the body will become more and more prevalent in near-future technology. Such "implantable bioelectronics" are envisaged as having a wide range of uses ...

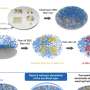
The chemical composition of human sweat tells us a lot about our health, but collecting it for analysis can be tricky. Current devices worn on the skin fill reservoirs one at a time but do not reflect how our rate of sweating ...
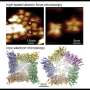
A member of an important class of ion channel proteins can transiently rearrange itself into a larger structure with dramatically altered properties, according to a study led by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine. The ...

A few years ago while on a fishing trip in the Florida Keys, biologist Lori Schweikert came face to face with an unusual quick-change act. She reeled in a pointy-snouted reef fish called a hogfish and threw it onboard. But ...

New Stanford University research has revealed that the mineral silica, a common food additive and popular cosmetics ingredient, is not a chemically inert substance, as has long been supposed.

Scientists have identified a molecule that plays a key role in how cells detect when they are being pushed or pulled which could lead to the development of future drugs for obesity, osteoporosis, and inflammatory diseases.

Physicists like me don't fully understand what makes up about 83% of the matter of the universe—something we call "dark matter." But with a tank full of xenon buried nearly a mile under South Dakota, we might one day be ...

Engineers have developed nanoscale tattoos—dots and wires that adhere to live cells—in a breakthrough that puts researchers one step closer to tracking the health of individual cells.