Last update:
Plasma Physics news

ATLAS observes top quarks in lead–lead collisions
At a talk held at CERN this week, the ATLAS collaboration at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) reported observing top quarks in collisions between lead ions, marking the first observation of this process in interactions between ...
General Physics
3 hours ago
0
1

New family of optimized magnetic fields could display enhanced fusion plasma confinement
Physicists have been trying to design fusion reactors, technologies that can generate energy via nuclear fusion processes, for decades. The successful realization of fusion reactors relies on the ability to effectively confine ...

Kinetic Alfvén waves may be key to mystery of solar corona heating
Syed Ayaz, a researcher at The University of Alabama in Huntsville (UAH), has published a paper in Scientific Reports that builds on an earlier first-of-its-kind study that examined kinetic Alfvén waves (KAW) as a possible ...
Plasma Physics
22 hours ago
0
52

Study identifies promising materials for fusion reactors
Nuclear fusion could be an ideal solution to mankind's energy problem, guaranteeing a virtually limitless source of power without greenhouse gas emissions. But there are still huge technological challenges to overcome before ...
Plasma Physics
Nov 5, 2024
0
89

Ensuring a bright future for diamond electronics and sensors by perfecting the growth process
Researchers are developing new ideas about the best ways to make lab-grown diamonds while minimizing other forms of carbon, such as soot. These diamonds aren't destined for rings and necklaces, though. These are the kinds ...
Condensed Matter
Nov 5, 2024
0
23

For heating plasma in fusion devices, researchers unravel how electrons respond to neutral beam injection
Heating a plasma for fusion research requires megawatts of power. One approach that research tokamaks use to achieve the necessary power input is neutral beam injection (NBI). With NBI, fast neutral particles are generated ...
Plasma Physics
Oct 25, 2024
0
0

Nuclear fusion energy requires heat- and radiation-resilient materials to be reliable, says nuclear engineer
Fusion energy has the potential to be an effective clean energy source, as its reactions generate incredibly large amounts of energy. Fusion reactors aim to reproduce on Earth what happens in the core of the sun, where very ...
Plasma Physics
Oct 21, 2024
6
47

In a fusion device plasma, a steep ion temperature gradient slows the growth of magnetic islands
Future fusion power plants will require good plasma confinement to sustain reactions and generate energy. One way to contain plasma for fusion reactions is to use a tokamak, a device that applies magnetic fields to "bottle" ...
Plasma Physics
Oct 15, 2024
0
29

Researchers uncover role of plasma waves in mysterious heating of sun's corona
There is a profound mystery in our sun. While the sun's surface temperature measures around 10,000 degrees Fahrenheit, its outer atmosphere, known as the solar corona, measures more like 2 million degrees Fahrenheit, about ...
Plasma Physics
Oct 11, 2024
1
137

New AI models of plasma heating lead to important corrections in computer code used for fusion research
New artificial intelligence (AI) models for plasma heating can do more than was previously thought possible, not only increasing the prediction speed 10 million times while preserving accuracy, but also correctly predicting ...
Plasma Physics
Oct 9, 2024
0
63

Neural networks boost fusion research with rapid ion temperature and rotation velocity predictions
In fusion experiments, understanding the behavior of the plasma, especially the ion temperature and rotation velocity, is essential. These two parameters play a critical role in the stability and performance of the plasma, ...
Plasma Physics
Oct 8, 2024
0
38

Stopping off-the-wall behavior in fusion reactors
Fusion researchers are increasingly turning to the element tungsten when looking for an ideal material for components that will directly face the plasma inside fusion reactors known as tokamaks and stellarators. But under ...
Plasma Physics
Oct 7, 2024
0
45

A new and unique fusion reactor comes together due to global research collaboration
Like atoms coming together to release their power, fusion researchers worldwide are joining forces to solve the world's energy crisis. Harnessing the power of fusing plasma as a reliable energy source for the power grid is ...
Plasma Physics
Sep 30, 2024
0
242

Researchers build AI model database to find new alloys for nuclear fusion facilities
A study led by the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory details how artificial intelligence researchers have created an AI model to help identify new alloys used as shielding for housing fusion applications ...
General Physics
Sep 19, 2024
0
202

Tracking plasma progression in a picosecond: Physicists develop ultra-fast laser method to study high-density plasmas
In a few picoseconds (trillionths of a second), a small, thin piece of copper momentarily becomes dense plasma, specifically a state called warm dense matter, warm being a relative term—the metal is nearly 200,000 degrees ...
Plasma Physics
Sep 18, 2024
0
113

AI enhances plasma plume analysis
In a published in the journal npj Computational Materials, Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists developed a deep learning model—a type of artificial intelligence that mimics human brain function—to analyze high-speed ...
Plasma Physics
Sep 16, 2024
0
13

Measuring the gamma-ray-to-neutron branching ratio in the deuterium-tritium reaction
Magnetic confinement fusion devices are technologies that can attain controlled nuclear fusion reactions, using magnetic fields to confine hot plasmas. These devices could contribute to the ongoing transition towards more ...

Researchers present new diagnostic tool for laser-plasma accelerator using metal foil as 3D scanner
Laser-plasma accelerators take up less space than conventional facilities, which are sometimes kilometers long. Such compact particle sources can accelerate electron bunches efficiently, enabling X-ray lasers that fit in ...
Optics & Photonics
Aug 30, 2024
0
70

Bubbling, frothing and sloshing: Long-hypothesized plasma instabilities finally observed
Whether between galaxies or within doughnut-shaped fusion devices known as tokamaks, the electrically charged fourth state of matter known as plasma regularly encounters powerful magnetic fields, changing shape and sloshing ...
Plasma Physics
Aug 27, 2024
1
169

How particles of light may be producing drops of the perfect liquid
The world's largest and most powerful particle accelerator may be producing the world's tiniest droplets of liquid, right under scientists' noses. Researchers are digging into this subatomic enigma.
General Physics
Aug 22, 2024
2
18
More news

3D visualization brings nuclear fusion to life

New AI program helps identify elusive space plasmoids
Other news

Novel magnetic field integration enhances green hydrogen peroxide production

Study uncovers role of tissue viscoelasticity in cell response

Scientists propose drug-free method to combat antibiotic-resistant bacteria

Hormone receptor structure reveals how it functions in heart disease
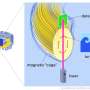
The discovery of new turbulence transition in fusion plasmas
Researchers create the world's strongest ionizing terahertz radiation

Physicists create the first fully mechanical qubit

New route to quantum spin liquid materials discovered