Last update:
Condensed Matter news

Findings hint at a superfluid phase in ²⁹F and ²⁸O
Data collected by the SAMURAI spectrometer at RIKEN's RI Beam Factory (RIBF) in Japan recently led to the detection of a rare fluorine (F) isotope, known as 30F. This has opened interesting possibilities for the study of ...

Antiferromagnetic spintronics advance opens door to next-gen electronics
University of Nebraska–Lincoln researchers have achieved a breakthrough in antiferromagnetic spintronics, a development that could expand the nanotechnology's capabilities, which have been limited by their need for excessive ...
Condensed Matter
23 hours ago
0
10

Zirconium metals under extreme conditions found to deform in surprisingly complex ways
Materials are crucial to modern technology, especially those used in extreme environments like nuclear energy systems and military applications. These materials need to withstand intense pressure, temperature and corrosion. ...
Condensed Matter
Sep 17, 2024
0
65

Quantum tech breakthrough could enable precision sensing at room temperature
A breakthrough in quantum technology research could help realize a new generation of precise quantum sensors that can operate at room temperature.
Condensed Matter
Sep 17, 2024
0
65

Tunable nonlinear Hall effect observed at room temperature in tellurium
A research team has discovered significant nonlinear Hall and wireless rectification effects at room temperature in elemental semiconductor tellurium (Te). Their research is published in Nature Communications.
Condensed Matter
Sep 16, 2024
0
63

New strategy for simulating nonadiabatic dynamics of molecules at metal surfaces
A research team has proposed a novel approach to accurately describe electron transfer mediated nonadiabatic dynamics of molecules at metal surfaces. Their works were published in Physical Review Letters.
Condensed Matter
Sep 16, 2024
0
20

Energy-saving computing with magnetic whirls
Researchers at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) have managed to enhance the framework of Brownian reservoir computing by recording and transferring hand gestures to the system that then used skyrmions to detect these ...
General Physics
Sep 16, 2024
0
73

Generating spin currents directly using ultrashort laser pulses
An international team of physicists has found that it is possible to generate spin currents directly using certain kinds of ultrashort laser pulses. In their study, published in the journal Physical Review Letters, the group ...

Fundamental spintronics research reveals generic approach to magnetic second-order topological insulators
Researchers from Monash University, part of the FLEET Center, have revealed a generic approach towards intrinsic magnetic second-order topological insulators. These materials are crucial for advancements in spintronics, an ...
Condensed Matter
Sep 12, 2024
0
36

Wave scattering simulation unlocks potential metamaterials
A new software package developed by researchers at Macquarie University can accurately model the way waves—sound, water or light—are scattered when they meet complex configurations of particles.
Condensed Matter
Sep 12, 2024
0
57

Overcoming magnetic disorder: Toward low-energy topological electronics
Overcoming magnetic disorder is key to exploiting the unique properties of quantum anomalous Hall (QAH) insulators. A Monash-led team has demonstrated that the breakdown in topological protection is caused by magnetic disorder, ...
Condensed Matter
Sep 11, 2024
0
33

Strong magnetic second harmonic generation effect discovered in two-dimensional CrPS₄ monolayer
A research team led by Professor Sheng Zhigao at the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has, for the first time, observed the strong nonlinear magnetic second harmonic generation (MSHG) ...
Condensed Matter
Sep 10, 2024
0
87

Unprecedented spin properties revealed in new artificial materials
In conjunction with research staff from the Charles University of Prague and the CFM (CSIC-UPV/EHU) center in San Sebastian, CIC nanoGUNE's Nanodevices group has designed a new complex material with emerging properties in ...
Condensed Matter
Sep 10, 2024
0
144

Why do materials get stronger when they are deformed? Research sheds light on universal mechanisms of work hardening
The earliest blacksmiths in the Bronze and Iron Ages figured out that when they deformed metal through bending or hammering, it became stronger. This process, known as work or strain hardening, is still used widely in metallurgy ...
Condensed Matter
Sep 9, 2024
0
31

Researchers advance new class of quantum critical metal that could advance electronic devices
A new study led by Rice University's Qimiao Si has unveiled a new class of quantum critical metal, shedding light on the intricate interactions of electrons within quantum materials. Published in Physical Review Letters on ...
Condensed Matter
Sep 6, 2024
0
200

Unlocking the secrets of diamond: New insights into nitrogen-vacancy center formation
Research teams from Wuhan University and the China University of Geosciences (Wuhan) have revealed new insights into the formation mechanism of nitrogen-vacancies (NV) centers in type-Ib diamonds, a phenomenon critical to ...
Condensed Matter
Sep 6, 2024
0
1

Physicists capture images of atoms flowing along a boundary without resistance despite obstacles in their path
Typically, electrons are free agents that can move through most metals in any direction. When they encounter an obstacle, the charged particles experience friction and scatter randomly like colliding billiard balls.
Condensed Matter
Sep 6, 2024
0
180

Nuclear fuel experiment demonstrates how liquid plutonium oxide behaves at the hottest temperatures
The 2011 accident at the Fukushima-Daiichi plant in Japan inspired extensive research and analysis that elevated nuclear energy into a standard bearer for safety. It also inspired a number of studies at the U.S. Department ...
Condensed Matter
Sep 5, 2024
0
107

Adding an alternating magnetic field to layers of twisted graphene creates even more exotic properties
Magnetic fields can engineer flat bands in twisted graphene layers to create a new playground for exotic physics, RIKEN physicists have shown.
Condensed Matter
Sep 5, 2024
0
23

Physicists capture first thickness-dependent transitions in two-dimensional magnetic material
A team of physicists from The University of Hong Kong (HKU), Texas Tech University (TTH), and the University of Michigan (UMich), has made an important discovery in the study of van der Waals (vdW) magnetic materials, a special ...
Condensed Matter
Sep 5, 2024
0
116
More news

Creating an 'imprint' on a super photon

Physicists predict existence of new exciton type

Sound drives 'quantum jumps' between electron orbits

Scientists uncover exciton behavior in van der Waals magnets
Physicists uncover new phenomena in fractional quantum Hall effects

A new approach to fine-tuning quantum materials
New research challenges conventional wisdom on wet surface adhesion

Can quantum particles mimic gravitational waves?
'Kink state' control may provide pathway to quantum electronics
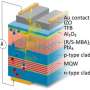
'Miracle' filter turns store-bought LEDs into spintronic devices

Gene-based model predicts when Japan's cherry buds awake from dormancy

Why petting your cat leads to static electricity

Can toddlers help explain the origins of our bias for wealth?