Materials Science
Researchers zero in on the underlying mechanism that causes alloys to crack when exposed to hydrogen-rich environments
When deciding what material to use for infrastructure projects, metals are often selected for their durability. However, if placed in a hydrogen-rich environment, like water, metals can become brittle and fail. Since the ...
1 hour ago
0
0
Social Sciences
International study highlights large and unequal life expectancy declines in India during COVID-19
A new paper published in Science Advances today finds that life expectancy in India was 2.6 years lower in 2020 than 2019, with women and marginalized social groups suffering the greatest declines.
4 hours ago
0
0

Enhanced information in national policies can accelerate Africa's efforts to track climate adaptation
New analysis of African national adaptation policy documents finds that most fail to provide comprehensive and consistent information. But the authors also uncover compelling examples ...
New analysis of African national adaptation policy documents finds that most fail to provide comprehensive and consistent information. But the authors ...
Environment
4 hours ago
0
0

Global study demonstrates benefit of marine protected areas to recreational fisheries
Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) are having a positive spillover effect, producing more "trophy-size" fish just outside of the fully protected areas, and the effect is growing stronger ...
Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) are having a positive spillover effect, producing more "trophy-size" fish just outside of the fully protected areas, and ...
Ecology
4 hours ago
0
0

Killifish can adjust their egg-laying habits in response to predators, study shows
Some species of fish can change their egg-laying habits in response to predators in the area in order to survive, according to new research from The University of Texas at Arlington.
Some species of fish can change their egg-laying habits in response to predators in the area in order to survive, according to new research from The University ...
Evolution
4 hours ago
0
7

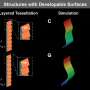
Innovative microscopy reveals amyloid architecture, may give insights into neurodegenerative disease
Amyloid-beta (A-beta) aggregates are tangles of proteins most notably associated with neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's. Despite its constant stint in the limelight, however, researchers have been unable to get ...
Bio & Medicine
5 hours ago
0
56

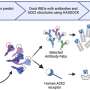
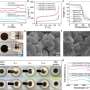
Study deciphers intricate 3D structure of DNA aptamer for disease theranostics
In a study published in PNAS, a research team has resolved the first high-resolution structure of the sgc8c DNA aptamer that targets protein tyrosine kinase 7 (PTK7), engineered two optimal sgc8c variants for disease theranostics ...
Molecular & Computational biology
6 hours ago
0
10
Researchers use light to control ferrofluid droplet movements in water
A team of engineers at the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems, the Chinese University of Hong Kong and the Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology has found that ferrofluidic drops in a tank of water can be ...

New framework allows robots to learn via online human demonstration videos
To be successfully deployed in real-world settings, robots should be capable of reliably completing various everyday tasks, ranging from household chores to industrial processes. Some of the tasks they could complete entail ...

How well does Medicare cover end-of-life care? It depends on what type
Not all versions of Medicare are created equal—and when it comes to end-of-life care, some versions may serve a patient's needs better than others. That's the focus of newly published research by Lauren Hersch Nicholas, ...
Medical economics
4 hours ago
0
25

Computational tool integrates transcriptomic data to enhance breast cancer diagnosis and treatment
Addressing problems with diagnosing and treating breast cancer, scientists at EPFL have developed EMBER, a tool that integrates breast cancer transcriptomic data from multiple databases. EMBER can improve precision oncology ...
Oncology & Cancer
5 hours ago
0
6
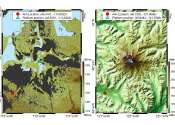
Enhancing adaptive radar with AI and an enormous open-source dataset
The world around us is constantly being flash photographed by adaptive radar systems. From salt flats to mountains and everything in between, adaptive radar is used to detect, locate and track moving objects. Just because ...
Engineering
5 hours ago
0
45

Engineers eliminate surface concavities to produce more efficient and stable perovskite solar cells
A research team from the School of Engineering of the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has shown the existence of surface concavities on individual crystal grains, which are the fundamental building ...
Energy & Green Tech
5 hours ago
0
14

The Future is Interdisciplinary
Find out how ACS can accelerate your research to keep up with the discoveries that are pushing us into science’s next frontier
 Medical Xpress
Medical Xpress
How well does Medicare cover end-of-life care? It depends on what type
90-day prescriptions lead to better blood pressure outcomes in children

Pandemic health behaviors linked to rise in neonatal health issues
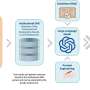
Making clinical guidelines work for large language models

Study suggests prenatal diet may play a role in autism

Researchers learn how cancer cells divide despite treatment

Study finds tumor growth fueled by nucleotide salvage

Study shows promise for a universal influenza vaccine: Scientists validate theory using 1918 flu virus

High stress during pregnancy linked to elevated cortisol in toddlers' hair

Eliminating senescent cells could help treat breast, pancreatic cancers

Fewer mental health facilities offering telehealth since end of pandemic

Historical smallpox vaccination may confer some protection against mpox disease

Researcher: Meditation can be harmful—and can even make mental health problems worse
 Tech Xplore
Tech Xplore

Neural network learns to build maps using Minecraft

New humidity-driven membrane removes carbon dioxide from the air

Can consciousness exist in a computer simulation?

Renewable electricity to outstrip coal next year: IEA

A new method to fabricate stretchable and breathable electronics

Engineers develop OptoGPT for improving solar cells, smart windows, telescopes and more

Study shows new truck efficiency standards may reduce expected energy savings

Researchers develop novel electrode for improving flowless zinc-bromine battery

Gold co-catalyst improves photocatalytic degradation of micropollutants, finds study
To remove micropollutants such as pesticides and trace chemicals from the environment, you need something equally small and cunning. One potential method is photocatalysis, which uses semiconducting nanomaterials powered ...
Analytical Chemistry
6 hours ago
0
25

Pandemic health behaviors linked to rise in neonatal health issues
Studies show that social distancing and other public health measures during the COVID-19 pandemic effectively reduced the spread of the deadly virus. However, they had unanticipated effects such as reduced health care accessibility ...
Obstetrics & gynaecology
5 hours ago
0
64

New dawn for space storm alerts could help shield Earth's tech
Space storms could soon be forecast with greater accuracy than ever before thanks to a big leap forward in our understanding of exactly when a violent solar eruption may hit Earth.
Astronomy
7 hours ago
0
30

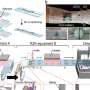
How mantle hydration changes over the lifetime of a subduction zone
Because of interactions with Earth's hot mantle, water-logged oceanic plates release water as they slide beneath less dense overriding plates in subduction zones. This water rises and hydrates the mantle above it, contributing ...
Earth Sciences
7 hours ago
0
38

A new way to control the magnetic properties of rare earth elements
The special properties of rare earth magnetic materials are due to the electrons in the 4f shell. Until now, the magnetic properties of 4f electrons were considered almost impossible to control.
Condensed Matter
7 hours ago
0
77
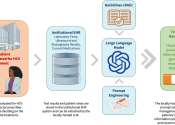
Making clinical guidelines work for large language models
Clinical guidelines are essential to the practice of evidence-based medicine, but they are long and complex, which makes it hard for busy doctors to quickly and easily find the information they need to care for each patient.
Health informatics
6 hours ago
0
27

Giant millipede was lost to science for 126 years: It's just been found in Madagascar
When a new species is discovered in the depths of the rainforest or on top of a mountain, it can be years before the creature is cataloged again. Separated from science by elevation, water or tangled branches, the species ...
Plants & Animals
7 hours ago
0
1

Chemists design novel method for generating sustainable fuel
Chemists have been working to synthesize high-value materials from waste molecules for years. Now, an international collaboration of scientists is exploring ways to use electricity to streamline the process.
Analytical Chemistry
7 hours ago
0
10
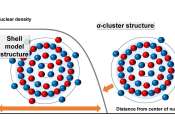
Results suggests titanium-48's nuclear structure changes when observed at varying distances
The world around us is made up of particles invisible to the naked eye, but physicists continue to gain insights into this mysterious realm. Findings published in Physical Review C by Osaka Metropolitan University researchers ...
General Physics
9 hours ago
2
44

Rhythmic gene expression in plants is crucial for symbiosis with nutrient-providing bacteria, study finds
Legumes thrive in low-nitrogen environments by partnering with rhizobia, soil bacteria that convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonium, a usable form for the plants. These beneficial bacteria are housed in root nodules formed ...
Plants & Animals
7 hours ago
0
33

US to phase out federal purchase of single-use plastics
President Joe Biden's administration on Friday announced plans to phase out single-use plastics in all federal operations by 2035, as part of a broader effort to combat what it deemed a rising global crisis.

Humans caused climate change. Amid the suffering, now they must solve it
For decades, scientists warned that continued burning of oil, gas, and coal would have devastating climate impacts. Those impacts are being felt around the world.

Seasonal menace: Protecting livestock against external parasites
While rain followed by sunshine produces the eye-catching sight of a rainbow, it can also mark the need for livestock owners to confront the insects and parasites that thrive in the summer season.

Hubble views a potential galactic merger
This NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image features the dwarf irregular galaxy NGC 5238, located 14.5 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Canes Venatici. Its unexciting, blob-like appearance seems to resemble ...
UK study finds urban residents score the lowest in social and economic satisfaction and well-being
A study conducted by the Center for Urban Mental Health at the University of Amsterdam finds that, in a sample of 156,000 UK residents aged 40 and up, urban living is linked to lower levels of well-being, social satisfaction, ...

Moon fests, moon movie and even a full moon mark 55th anniversary of Apollo 11 landing
The cosmos is providing a full moon for the 55th anniversary of the first lunar landing this weekend, and plenty of other events honor Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin's giant leap.

Mexico tries to bring drought-stricken lake back to life
Mexican authorities are releasing thousands of juvenile fish and cleaning up freshwater springs as part of efforts to rejuvenate one of the country's lakes stricken by drought and heat waves.

COP29 hosts urge fossil fuel majors to donate to climate fund
Azerbaijan said Friday it hopes to raise money from fossil fuel producers for green projects in developing countries as the petro-state prepares to host the world's most important climate summit.

Elevated levels of antibiotic resistance genes should be considered a new factor of global change, researchers say
Human-caused global change is a complex phenomenon comprising many factors such as climate change, environmental contamination with chemicals, microplastics, light pollution, and invasive plants. One of the main tasks of ...

Deeper down the rabbit hole: How technology conspiracy beliefs emerge and foster a conspiracy mindset
As technology proliferates, misinformation and conspiracy theories seem to flourish. Conspiracy beliefs specifically about technology include popular commercial technologies, such as Amazon Echo and Google Search, as well ...

Smallholder farmers, efficient ranching practices critical to meet restoration targets in Brazil's Atlantic Forest
A new study led by King's College London simulated the effects of various restoration policies to assess their impact on biodiversity and agricultural production.

Cooling must be seen as critical national infrastructure, new report says
A Cranfield University academic has contributed to a new landmark report that says that governments and policy makers must recognize cooling as critical national infrastructure (CNI) if humanity is to build resilience to ...

'My brain leaves the room': what happens when teachers talk too much?
About four students in every classroom will have a language or attention disorder. While some of these students will have an official diagnosis of developmental language disorder (DLD) or attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder ...

Washington DC among US cities most vulnerable to space weather, scientists say
Several cities in the United States—including the nation's capital—have power grids particularly vulnerable to the threat of space weather—but experts are still trying to understand why.
Research team reconstructs evolutionary history and biological adaptation of Han Chinese people on the Mongolian Plateau
A Chinese research team analyzed 5,583 modern and ancient individuals from an integrated genomic dataset to reconstruct the population evolutionary history and biological adaptation of the Han Chinese population across the ...

How nature-based solutions can promote effective flood management
This week, large areas of Ontario experienced severe flooding that caused widespread power outages, water damages and disruption. Severe rainfall events are not new, but they are becoming more frequent and costly due to human-caused ...

Researchers see lower meat consumption after veggie month at student canteen
What effect does a vegan/vegetarian month have on a student canteen? For this experiment, the Studierendenwerk Bonn sought scientific support from researchers at the Universities of Bonn and Kassel. They found that the impact ...

Wetland wonders unfold: Aerial systems shed light on ecosystem services
Coastal wetlands, situated at the junction of land and water, are vital ecosystems known for their high productivity. They play a key role in carbon sequestration, storm buffering, and providing habitats for diverse species. ...

'Diagnose, treat and prevent:' Scientists develop test and vaccine for common veterinary infection
Eight years after the market release of VANGUARD crLyme, a first-of-its-kind vaccine designed to prevent Lyme disease in dogs, the Marconi laboratory in the Department of Microbiology and Immunology of the Virginia Commonwealth ...

Critically endangered Guam tree contributes to global leaf research
The intricate leaf design of Guam's Serianthes nelsonii tree was used as a model to contribute to the global goal of understanding how a plant leaf functions, and the results were published in the March issue of the journal ...