This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Combined effects of plastic pollution and seawater flooding amplify threats to coastal plant species
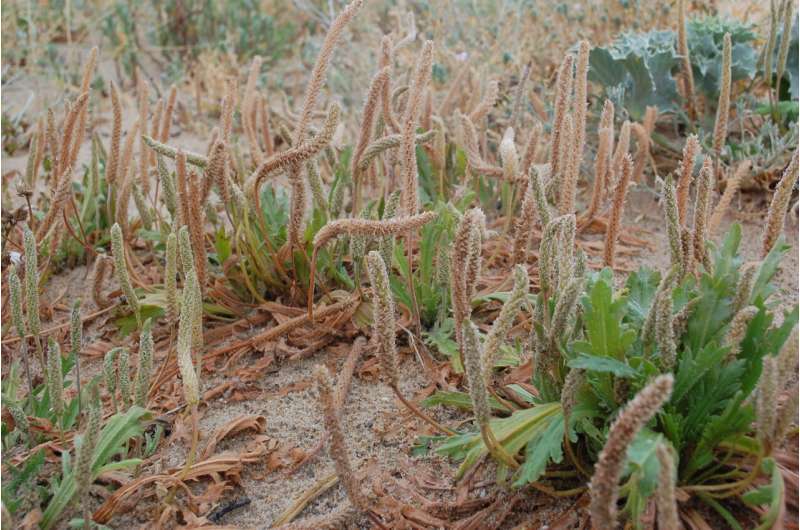

Two of the planet's more pressing environmental stressors have the potential to alter the growth and reproductive output of plants found right along the world's coastlines, a new study suggests.
The research, published in the journal Environmental Pollution, is one of the first to examine the combined effects of seawater flooding and microplastic pollution on coastal plants.
It showed that both stressors had some effects on the species tested, with microplastics impacting the plants' reproduction while flooding caused greater tissue death.
However, being exposed to both microplastics and flooding together—a threat likely to increase as a result of climate change and plastic use—had a more pronounced impact on their resource allocation.
This in turn led to the plants exhibiting altered growth and experiencing short-term suppression in their photosynthetic efficiency. Responses affect the plants' ability to capture water, nutrients and sunlight, and contribute to ecosystem well-being.
The study was led by experts in plastic pollution and plant biology from the University of Plymouth's School of Biological and Marine Sciences and International Marine Litter Research Unit.
They say it signposts the potential for microplastics to present an elevated risk when in combination with additional stressors like seawater flooding and that, as a result, establishing the threats presented by multiple co-occurring stressors on ecosystem resilience is a priority.
Dr. Winnie Courtene-Jones, the study's lead author, said, "This research highlights the potential for microplastics, composed of conventional and biodegradable plastic, to detrimentally affect plant functioning. More-so, it indicates that the effect of microplastics can be magnified by other environmental factors such as rising sea levels and coastal flooding. Studies such as this help us appreciate the potential harm posed by microplastics to a range of organisms, and ecosystem resilience generally."
The study was carried out as part of BIO-PLASTIC-RISK, a £2.6million project led by the University.
It focused on buck's horn plantain (Plantago coronopus), a low-growing perennial native to Europe, Asia and North Africa—but also found in the United States, Australia, and New Zealand—which commonly grows in sand dune and beach shingle coastal habitats.
Plants were grown in soil containing conventional or biodegradable plastics for 35 days before being flooded with seawater for 72 hours, replicating the kinds of flooding event increasingly associated with storms and coastal storm surges.
They were then grown for a further 24 days with scientists monitoring plant survival in addition to factors such as plant size, photosynthetic efficiency and flower production.
Dr. Mick Hanley, Associate Professor in Plant-Animal Interactions and senior author on the study, added, "On a global scale, habitats such as coastal dunes and grasslands help protect communities in the form of coastal defenses and wind protection. They also play a critical role in supporting biodiversity, but are coming under increasing threat from climate change and a number of other environmental factors.
"This study emphasizes that we should not be looking at those threats in isolation as, put together, their impacts can be more pronounced. That is particularly worrying given that both microplastic pollution and coastal flooding are projected to worsen and intensify over the coming decades unless ambitious global actions are implemented."
More information: W. Courtene-Jones et al, Effect of biodegradable and conventional microplastic exposure in combination with seawater inundation on the coastal terrestrial plant Plantago coronopus, Environmental Pollution (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2024.124573
Journal information: Environmental Pollution
Provided by University of Plymouth