This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
To sound like a hockey player, speak like a Canadian
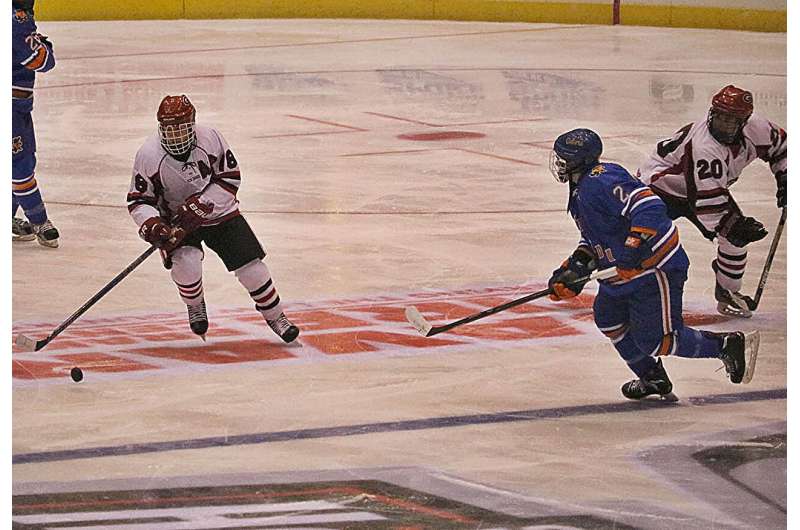

As a hockey player, Andrew Bray was familiar with the slang thrown around the "barn" (hockey arena). As a linguist, he wanted to understand how sport-specific jargon evolved and permeated across teams, regions, and countries. In pursuit of the sociolinguistic "biscuit" (puck), he faced an unexpected question.
"It was while conducting this initial study that I was asked a question that has since shaped the direction of my subsequent research," said Bray. "'Are you trying to figure out why the Americans sound like fake Canadians?'"
Canadian English dialects are stereotypically represented by the vowel pronunciation, or articulation, in words like "out" and "about," borrowed British terms like "zed," and the affinity for the tag question "eh?"
Bray, from the University of Rochester, presented an investigation into American hockey players' use of Canadian English accents May 16 at a joint meeting of the Acoustical Society of America and the Canadian Acoustical Association, held May 13–17 at the Shaw Center located in downtown Ottawa, Ontario, Canada.
Studying how hockey players talk required listening to them talk about hockey. To analyze unique vowel articulation and the vast collection of sport-specific slang terminology that players incorporated into their speech, Bray visited different professional teams to interview their American-born players.
"In these interviews, I would ask players to discuss their career trajectories, including when and why they began playing hockey, the teams that they played for throughout their childhood, why they decided to pursue collegiate or major junior hockey, and their current lives as professionals," said Bray. "The interview sought to get players talking about hockey for as long as possible."
Bray found that American athletes borrow features of the Canadian English accents, especially for hockey-specific terms and jargon, but do not follow the underlying rules behind the pronunciation, which could explain why the accent might sound "fake" to a Canadian.
"It is important to note that American hockey players are not trying to shift their speech to sound more Canadian," said Bray. "Rather, they are trying to sound more like a hockey player."
Players from Canada and northern American states with similar accents have historically dominated the sport. Adopting features of this dialect is a way hockey players can outwardly portray their identity through speech, called a linguistic persona. Many factors influence this persona, like age, gender expression, social category, and as Bray demonstrated, a sport.
Going forward, Bray plans to combine his recent work with his original quest to investigate if Canadian English pronunciation and the hockey linguistic persona are introduced to American players through the sport's signature slang.
More information: Technical program: https://eppro02.ativ.me/src/EventPilot/php/express/web/planner.php?id=ASASPRING24
Provided by Acoustical Society of America