April 12, 2024 report
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
New tidal stellar stream discovered with Gaia
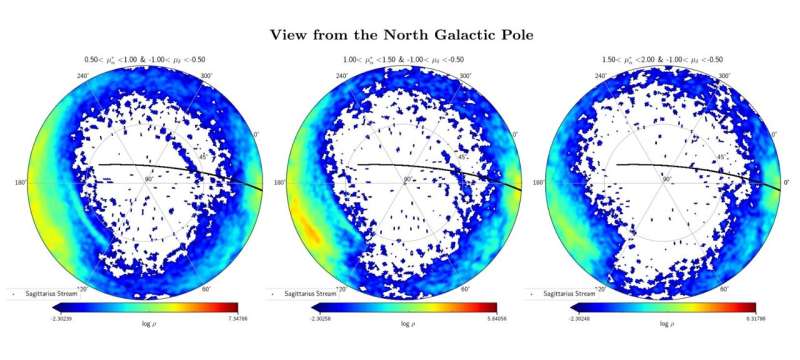
By analyzing the data from ESA's Gaia satellite, Chinese astronomers have detected a new tidal stellar stream in the northern hemisphere, which has a low metallicity and a relatively high energy. The finding was reported in a research paper published April 1 in The Astrophysical Journal.
In general, tidal stellar streams represent the remnants of ancient accretion events into a galaxy. Therefore, they could keep the memory of their progenitors' chemical and dynamical information, even after a few billion years. To date, more than 100 such structures have been identified, most of which are cold streams.
Recently, a team of astronomers led by Hao Tian of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have explored stellar substructures in the Milky Way's halo using astrometry from Gaia's Data Release 3 (DR3). As a result, they identified a new tidal stellar stream and derived its fundamental properties.
"Thanks to the precise astrometric measurements of proper motions by the Gaia mission, a new tidal stellar stream has been discovered in the northern hemisphere," the researchers wrote in the paper.
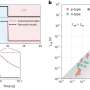
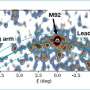
The new tidal stellar stream was found at a high Galactic latitude around 30–60 degrees with Galactic longitude from 270 to 30 degrees. The astronomers noted that although the surface density of this stream is very low, it is still significant compared to its neighborhood.
The newfound stream is approximately 80 degrees long and 1.7 degrees wide. By analyzing the spectra of seven member stars, it was found that the stream has a metallicity at a level of -1.3. This, together with the stream's large total energy and retrograde motion indicate that it is possibly associated with the merging event Sequoia.
All in all, the researchers investigated 21 members of the new stream, including 14 RR Lyrae stars. Based on this, they found that the stream has an eccentric orbit as its eccentricity is 0.58. Given that the stream has at least 14 known RR Lyrae stars, the scientists concluded that its progenitor should be of luminosity brighter than −6.9 mag.
Summing up the results, the authors of the paper underlined that further studies, mainly spectroscopic observations, are required in order to shed more light on the properties of the newly detected stellar stream. The discovery made by Tian's team is also promising in terms of finding new such structures in our galaxy.
"This discovery indicates that there should be more streams in the halo, which have not been discovered yet because of the observational and methodological limits, especially for those streams with highly radial orbits and low surface luminosity," the astronomers wrote.
More information: Hao Tian et al, A New Tidal Stream Discovered in Gaia DR3, The Astrophysical Journal (2024). DOI: 10.3847/1538-4357/ad2c06
Journal information: Astrophysical Journal
© 2024 Science X Network