This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
preprint
trusted source
proofread
TESS finds its first rogue planet
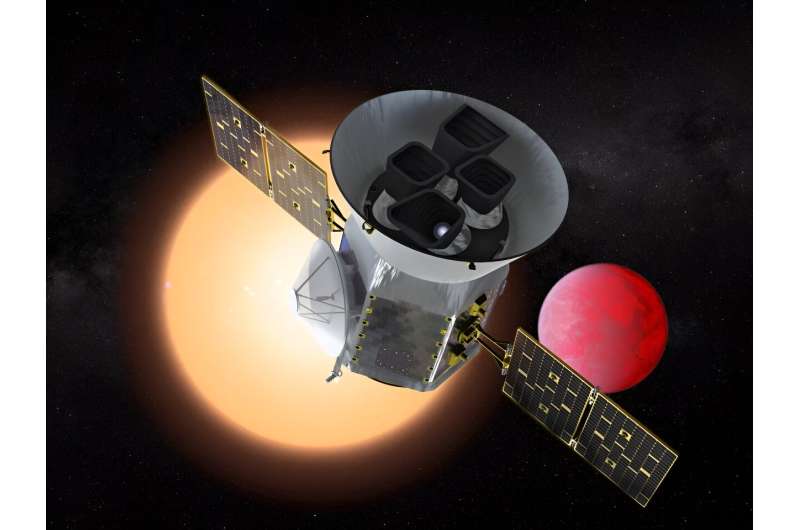

Well over 5,000 planets have been found orbiting other star systems. One of the satellites hunting for them is TESS, the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite. Astronomers using TESS think they are made a rather surprising discovery; their first free-floating—or rogue—planet. The planet was discovered using gravitational microlensing where the planet passed in front of a star, distorting its light and revealing its presence.
We are all familiar with the eight planets in our solar system and perhaps becoming familiar with the concept of exoplanets. But there is another category of planet, the rogue planets. These mysterious objects travel through space without being gravitationally bound to any star. Their origin has been cause for much debate but popular theory suggests they were ejected from their host star system during formation, or perhaps later due to gravitational interaction.
Simulations have suggested that these 'free-floating planets' or FFPs should be abundant in the galaxy yet until now, not many have been detected. The popular theory of ejection from star systems may not be the full story though.
It is now thought that different formation mechanisms will be responsible for different FFP masses. Those FFPs that are high mass may form in isolation from the collapse of gas while those at the low mass end (comparable to Earth) are likely to have been subjected to gravitational ejection from the system. A paper published in 2023 even suggests that those FFPs are likely to outnumber those bound planets across the galaxy.
Detecting such wandering objects among the stars is rather more of a challenge than you might expect. Their limited emission (or reflection) of electromagnetic radiation makes them pretty much impossible to observe. Enter gravitational microlensing, a technique that relies upon an FFP passing in front of a star, it's gravity then focusing light from the distant star resulting in a brief brightness change as the planet moves along its line of sight. To date, only three FFPs have been detected from Earth using this technique.
A team of astronomers have been using TESS to search for such microlensing events. TESS was launched in April 2018 and while in orbit, scans large chunks of sky to monitor the brightness of tens of thousands of stars. The detection of light changes may reveal the passage of an FFP as it drifts silently in front of the star. It's not an easy hunt though as asteroids in our solar system, exoplanets bound to stars and even stellar flares can all give false indications but thankfully the team led by Michelle Kunimoto have algorithms that will help to identify potential targets.
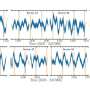
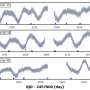
The team published their findings on the pre-print server arXiv and reported one FFP candidate event associated with the star TIC-107150013 which is 3.2 parsec away.
The event lasted 0.074 days +/- 0,002 and revealed a light curve with features expected of a FFP. This marks the first FFP discovered by TESS, an exciting step along the way to start to unravel the mysteries surrounding these strange alien worlds.
More information: Michelle Kunimoto et al, Searching for Free-Floating Planets with TESS: I. Discovery of a First Terrestrial-Mass Candidate, arXiv (2024). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2404.11666
Journal information: arXiv
Provided by Universe Today