This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
Researchers develop a new strategy to enhance blue perovskite LED performance
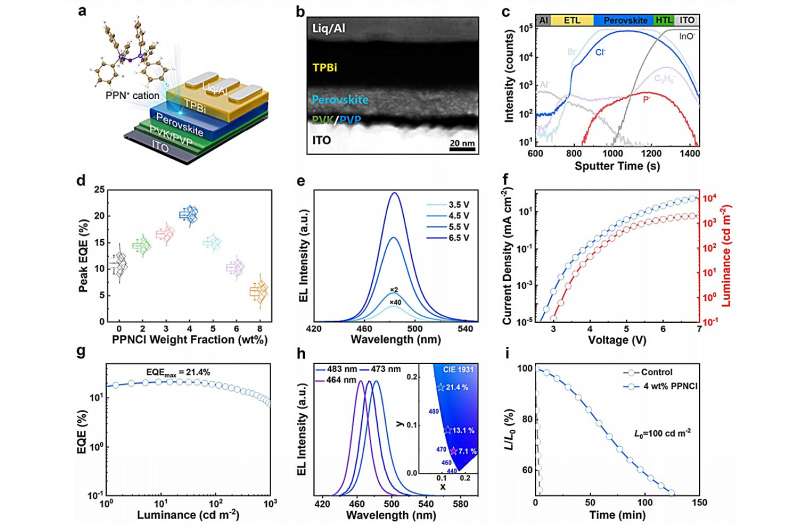
Prof. Cui Linsong's research team from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC), cooperating with Prof. Samuel D. Stranks' team from the University of Cambridge, devised a novel strategy to enhance the performance of blue light-emitting diodes (LEDs) based on perovskite materials. Their work has been published in Nature Photonics.
Perovskite LEDs have emerged as a promising next-generation technology for lighting and displays due to their superior luminescent properties and cost-effectiveness. While significant progress has been made in green, red, and near-infrared perovskite LEDs, the development of blue perovskite LEDs has lagged behind, posing a major bottleneck in the field.
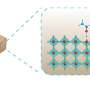
To address this challenge, the research team designed a multifunctional ionic additive, Bis(triphenylphosphine)iminium chloride (PPNCl), with multiple charged resonance forms and a dynamic electronic state. This compound enables precise control over the composition and distribution of perovskite phases, effectively suppressing non-radiative recombination channels and ion migration, thereby significantly improving the efficiency and stability of blue perovskite LEDs.
PPNCl interacts with the components of the perovskite via hydrogen bonding, influencing the crystallization process and favoring the transition to high-dimensional phases with enhanced luminescence efficiency.
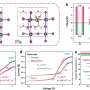
Transient absorption (TA) spectroscopy studies further revealed that PPNCl accelerates energy transfer processes from low-dimensional to high-dimensional phases, suppressing incomplete energy transfer and energy loss due to non-radiative recombination in low-dimensional phases.
Furthermore, PPNCl molecules coordinate with perovskite components and exhibit electrostatic interactions, effectively passivating defects in perovskite films and inhibiting halide ion migration, leading to a significant enhancement in the luminescence efficiency and spectral stability of perovskite films.
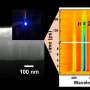
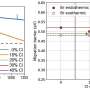
Thanks to the effective control exerted by PPNCl over perovskite phase distribution, defect states, and ion migration, high-efficiency and stable blue perovskite LEDs have been achieved. These devices exhibit a peak external quantum efficiency (EQE) of 21.4% (emission peak at 483 nm), marking the highest efficiency attained in blue perovskite LEDs to date. Additionally, the stability of the devices has been improved by nearly 30-fold.
This innovative achievement paves the way for further advancements in blue perovskite LED performance, signaling remarkable progress in perovskite LED technology.
More information: Shuai Yuan et al, Efficient blue electroluminescence from reduced-dimensional perovskites, Nature Photonics (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41566-024-01382-6
Journal information: Nature Photonics
Provided by University of Science and Technology of China