This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Key management practices to enhance biodiversity in the Western Pyrenees
A study in which the FisioKlima-AgroSosT group of the University of the Basque Country (UPV/EHU) participated identifies the key management practices needed to generate and maintain biodiversity in the grasslands of the Western Pyrenees of Navarre. The work was carried out in collaboration with the Government of Navarre and the company Gestión Ambiental de Navarra (GAN-NIK).
The findings are published in the Journal of Environmental Management.
Although European rural development and biodiversity conservation strategies have long recognized the importance of extensive high nature value livestock systems, many of these areas are now under threat of intensification and land abandonment.
The High Nature Value (HNV) concept or indicator encompasses all the agro-systems that are relevant to and contribute positively towards the conservation of biodiversity. Various pieces of work have been carried out to identify areas of high nature value at landscape scale. However, studies at the level of more basic management units, such as plots, are very scarce.
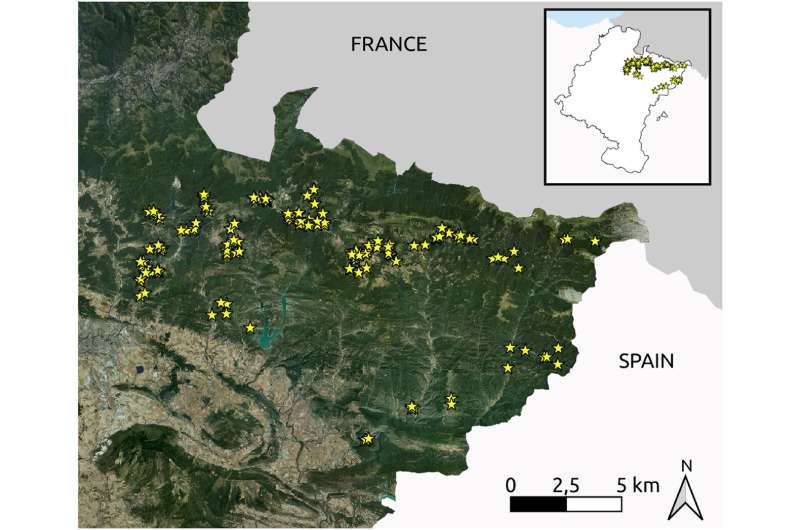
The UPV/EHU's FisioKlima-AgroSosT research group and collaborating organizations undertook an extensive field study at plot level. "When we are talking about plots, we are referring to the scale of units of management—pasture that has a single use and owner," explained Iker Pardo-Guereño, lecturer in the UPV/EHU's department of Plant Biology and Ecology.
To do this, "we studied around 144 plots in the Western Pyrenees of Navarre, and on the basis of that we developed a methodology to obtain an indicator of natural value. This indicator reflects how intensive the use is and what contribution it makes to biodiversity," said Iker Pardo.
This new indicator is based on multiple indices that together provide a more comprehensive assessment of biodiversity than conventional indicators such as species richness. In addition, "the data can be easily collected in the field, which provides an opportunity to involve non-specialists (e.g., farmers or livestock personnel) in assessing and monitoring the natural value of their own land or grassland," said the researcher.
Factors that contribute most towards enhancing biodiversity
The study concludes that "in the Western Pyrenees of Navarre the type of livestock emerges as an important factor determining the natural value of the grasslands. Plots grazed by horses, sheep or mixed herds of both yielded significantly more natural value than those grazed by cattle."
Pardo did however stress that "priority should be given to protecting and conserving extensively grazed plots that have not been treated (in terms of sowing and/or fertilizing) and which are already of high natural value. Agricultural policies should reinforce the restoration, maintenance and conservation of existing semi-natural meadows and grasslands and design interventions to prevent them from becoming abandoned or intensified.
"In the Pyrenees, many traditional meadows have been transformed into artificial meadowlands which, as this study shows, entails a substantial loss of natural value. So reversing this situation should be a priority," added the UPV/EHU researcher.
"Plots included in the Natura2000 network displayed significantly higher nature values than those outside the network. However, the contribution of the Natura network should be assessed in a time context, as it is likely that the condition of the plots located within the Natura 2000 spaces was already good by the time they were included in the network," said Pardo.
Although the nature value index was tested specifically for Pyrenean pastures, "This approach could be extended to any other livestock area or region by slightly adapting the indicators to the local context. The simplicity of the proposed field study method makes the index suitable for monitoring the success in terms of biodiversity of the practices that receive agri-environmental grants," added Pardo.
More information: Iker Pardo et al, Assessment of determinants of high nature value (HNV) farmland at plot scale in Western Pyrenees, Journal of Environmental Management (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.119516
Provided by University of the Basque Country