This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
reputable news agency
proofread
Japan 'Moon Sniper' lands but 'not generating power'
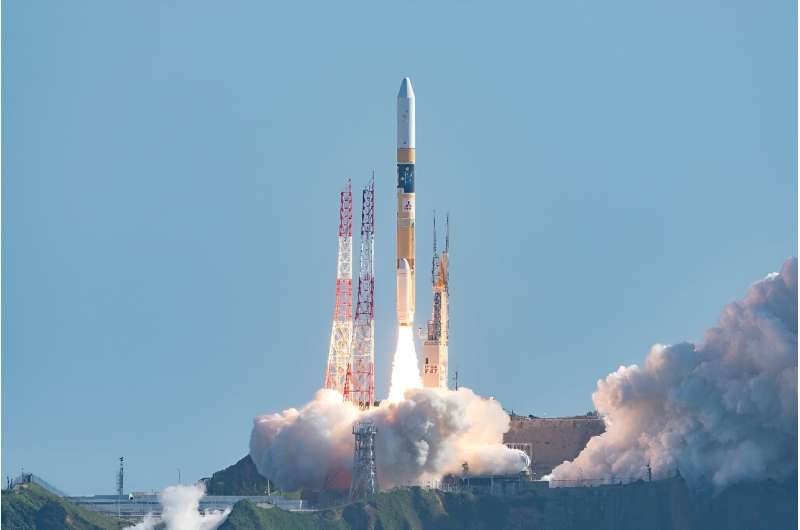

Japan on Saturday became only the fifth nation to achieve a soft Moon landing, but the craft's long-term fate was in doubt after space agency officials said its solar cells were not generating power.
With the Smart Lander for Investigating Moon (SLIM), Japan followed the United States, the Soviet Union, China and India in landing on the lunar surface.
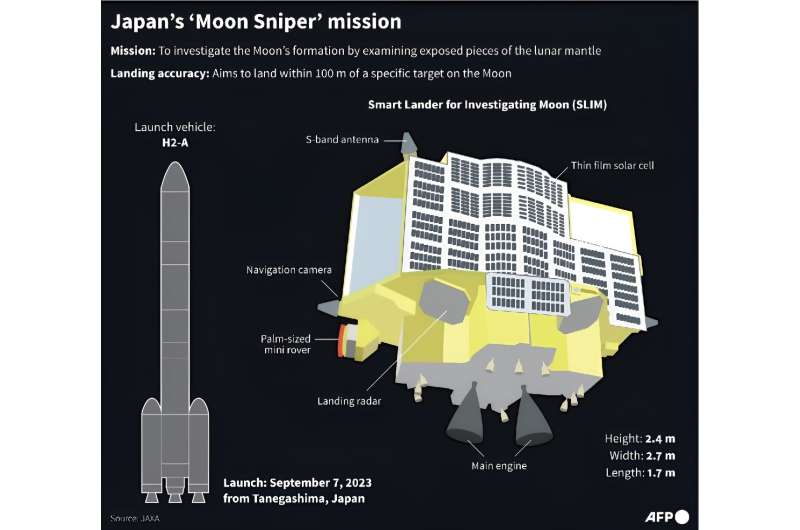
After initial uncertainty, space agency JAXA confirmed that the SLIM touched down on the Moon at 12:20 am Japanese time (1520 GMT Friday) and that "communication has been established".
JAXA official Hitoshi Kuninaka said that without the solar cells functioning, the craft would only have power for "several hours".
But he suggested that it was possible that once the angle of the sun changed, they may work again.
"It is unlikely that the solar battery has failed. It's possible that it is not facing in the originally planned direction," Kuninaka told a news conference.
"If the descent was not successful, it would have crashed at a very high speed. If that were the case, all functionality of the probe would be lost. But data is being sent to Earth," he said.
He added that for now, the focus was on using what power remained to send back to mission control all data that had been acquired during the landing.
This would include helping to determine whether the craft—dubbed the "Moon Sniper" for its precision—achieved the aim of landing within 100 meters (yards) of its intended landing spot.
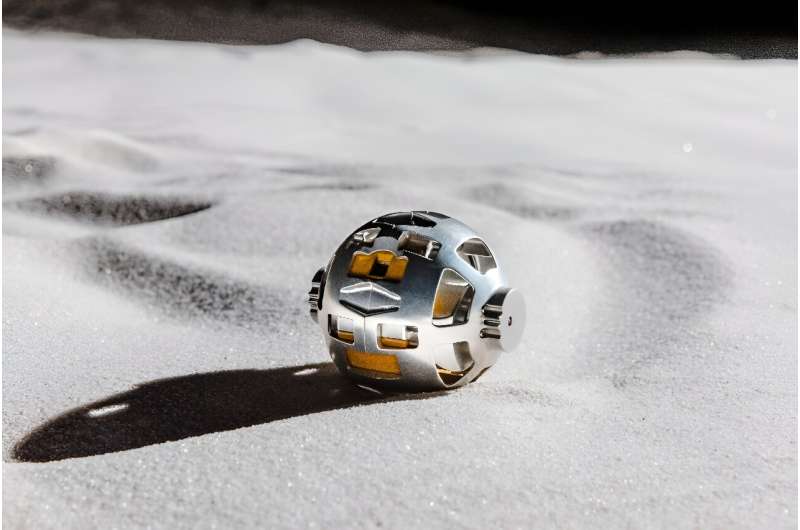
Two probes however detached successfully, JAXA said—one with a transmitter and another designed to trundle around the lunar surface beaming images back to Earth.
This shape-shifting mini-rover, slightly bigger than a tennis ball and inspired by how a turtle moves on a beach, was co-developed by the firm behind Transformer toys.

Mantle pieces
Japan's mission is one of a string of new projects launched in recent years on the back of renewed interest in Earth's natural satellite.
Success would restore high-tech Japan's reputation in space after two failed lunar missions and recent rocket failures, including explosions after take-off.
It would also echo the triumph of India's low-cost space program in August, when it became the first to land an uncrewed craft near the Moon's largely unexplored south pole.
SLIM was meant to try to reach a crater where the Moon's mantle—the usually deep inner layer beneath its crust—is believed to be accessible.
"The rocks exposed here are crucial in the search for the origins of the Moon and the Earth," Tomokatsu Morota, associate professor at the University of Tokyo specializing in lunar and planetary exploration, told AFP before the landing.
This includes shedding light on the mystery of the Moon's possible water resources, which will also be key to building bases there one day as possible stopovers on the way to Mars.
"The possibility of lunar commercialization depends on whether there is water at the poles," Morota said.
Renewed interest
More than 50 years after the first human Moon landing, many countries and private companies are attempting to make the trip anew.
But crash-landings, communication failures and other technical problems are rife.
This month, US private firm Astrobotic's Peregrine lunar lander began leaking fuel after takeoff, dooming its mission.
On Thursday, contact with the spaceship was lost over a remote area of the South Pacific after it likely burned up in the Earth's atmosphere on its return.
NASA has also postponed plans for crewed lunar missions under its Artemis program.
Russia, China and other countries from South Korea to the United Arab Emirates are also trying their luck.
Previous Japanese lunar missions have failed twice—one public and one private.
In 2022, the country unsuccessfully sent a lunar probe named Omotenashi as part of the United States' Artemis 1 mission.
In April, Japanese startup ispace tried in vain to become the first private company to land on the Moon, losing communication with its craft after what it described as a "hard landing".
© 2024 AFP





















