This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
reputable news agency
proofread
Repurposing dead spiders, counting cadaver nose hairs win Ig Nobels for comical scientific feats

Counting nose hairs in cadavers, repurposing dead spiders and explaining why scientists lick rocks, are among the winning achievements in this year's Ig Nobels, the prize for humorous scientific feats, organizers announced Thursday.
The 33rd annual prize ceremony was a prerecorded online event, as it has been since the coronavirus pandemic, instead of the past live ceremonies at Harvard University. Ten spoof prizes were awarded to the teams and individuals around the globe.
Among the winners was Jan Zalasiewicz of Poland who earned the chemistry and geology prize for explaining why many scientists like to lick rocks.
"Licking the rock, of course, is part of the geologist's and paleontologist's armory of tried-and-much-tested techniques used to help survive in the field," Zalasiewicz wrote in The Palaeontological Association newsletter in 2017. "Wetting the surface allows fossil and mineral textures to stand out sharply, rather than being lost in the blur of intersecting micro-reflections and micro-refractions that come out of a dry surface."
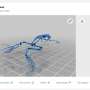
A team of scientists from India, China, Malaysia and the United States took the mechanical engineering prize for its study of repurposing dead spiders to be used in gripping tools.
"The useful properties of biotic materials, refined by nature over time, eliminate the need to artificially engineer these materials, exemplified by our early ancestors wearing animal hides as clothing and constructing tools from bones. We propose leveraging biotic materials as ready-to-use robotic components in this work due to their ease of procurement and implementation, focusing on using a spider in particular as a useful example of a gripper for robotics applications," they wrote in "Advanced Science" in July 2022.
Other winning teams were lauded for studying the impact of teacher boredom on student boredom; the affect of anchovies' sexual activity on ocean water mixing; and how electrified chopsticks and drinking straws can change how food tastes, according to the organizers.
The event is produced by the magazine "Annals of Improbable Research" and sponsored by the Harvard-Radcliffe Science Fiction Association and the Harvard-Radcliffe Society of Physics Students.
"Each winner (or winning team) has done something that makes people LAUGH, then THINK," according to the "Annals of Improbable Research" website.
© 2023 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed without permission.