This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
Probing rare hot plasma flows in the upper atmosphere
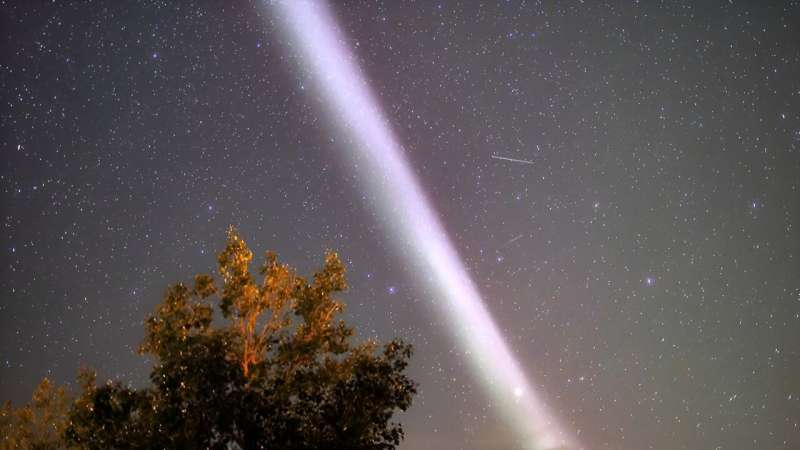

Near Earth's poles, observers of the night sky often behold aurorae, colorful light shows in the upper atmosphere caused by interactions between the solar wind and our planet's magnetosphere. A little closer to the equator, a different upper atmosphere phenomenon sometimes occurs: subauroral ion drifts (SAID).
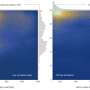
SAID events typically involve narrow, rapid, westward flows of extremely hot plasma—a mixture of charged particles—through the ionosphere. In recent years, scientists have linked SAID events with visible structures in the sky known as SAR (stable auroral red) arcs and STEVE (strong thermal emission velocity enhancement).
SAID events usually occur between dusk and midnight, but SAID flows have occasionally been detected after midnight. In a new study published in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, Horvath and Lovell take a closer look at the characteristics and formation of rare, postmidnight SAID events.
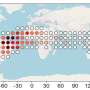
The researchers focused on 15 postmidnight SAID events detected near South America in 2013. To better understand them, they analyzed data from the Defense Meteorological Satellite Program, the Van Allen Probes, the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites, and various measures of auroral activity.
They found that much like premidnight SAID events, the 15 postmidnight events appear to have arisen from the complex interplay of ionospheric conditions and geomagnetic dynamics, including electric field formation and wave-particle interactions that serve as localized heat sources.
These findings provide new insights into upper atmosphere plasma dynamics and could help deepen understanding of the potential for SAID events to disrupt radar signals for satellite tracking and other critical applications.
More information: Ildiko Horvath et al, Antisunward Streaming Westward Sub‐Auroral Ion Drifts (SAID) Developed in the Postmidnight (1–4) Magnetic Local Time Sector During 2013, Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics (2023). DOI: 10.1029/2023JA031677
Provided by Eos
This story is republished courtesy of Eos, hosted by the American Geophysical Union. Read the original story here.