This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Faith primary schools admitting fewer children with special educational needs, study finds
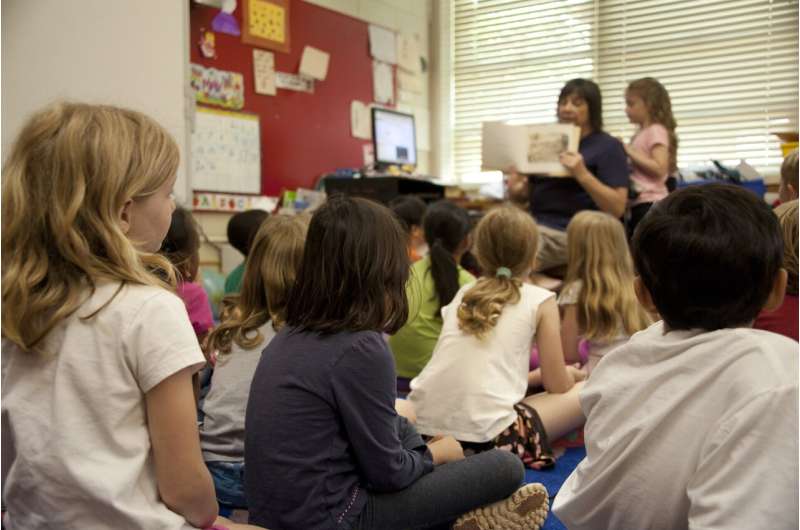

Faith primary schools are admitting fewer children with special educational needs and disabilities (SEND) than local authority community primaries, according to new research from the London School of Economics and Political Science (LSE).
Dr. Tammy Campbell analyzed Reception year admissions to mainstream state schools from 2010–2020 in England using the National Pupil Database census. She concluded that many faith primary schools "serve as hubs of relative advantage, seeming disproportionately to serve children from more affluent families and children less likely to have SEND."
"Serving their communities? The under-admission of children with disabilities and 'special educational needs' to 'faith' primary schools in England" by Dr. Campbell is published in Oxford Review of Education.
In 2020, Catholic schools admitted to Reception, on average, 24% fewer children with SEND recorded in pre-school than local authority community schools.
Church of England schools that administer their own admissions admitted, on average, 15% fewer children with SEND recorded in pre-school than local authority community schools.
And Church of England schools with centralized local authority admissions admitted, on average, 8% fewer children with SEND recorded in pre-school than local authority community schools.
Those with an Education, Health and Care Plan (EHCP), which is a higher-level SEND funded by local authorities, were also less likely to be admitted to faith schools.
In 2020, Catholic schools admitted, on average, 15% fewer children with higher-level, EHCP SEND than local authority community schools.
Church of England schools that administer their own admissions admitted, on average, 11% fewer children with higher-level, EHCP SEND than local authority community schools.
Church of England schools with centralized local authority admissions admitted, on average, 6% fewer children with higher-level, EHCP SEND than local authority community schools.
The analysis controls for other school-level factors, and the area in which the school is based.
Dr. Campbell's paper builds on previous research that suggests faith schools tend to educate proportionately fewer children from low-income families, following analysis of those in receipt of Free School Meals (FSM).
Her new analysis shows that when FSM and SEND are analyzed together, there is a "double effect." For example, in 2020, a child with SEND and FSM is estimated to have a 22% chance of attending a "faith" school, compared to a 29% chance for a child with no FSM eligibility nor pre-school SEND recorded. Those with an Education, Health and Care Plan (EHCP), the higher-level SEND funded by local authorities, had a 21% chance.
About 28% of state primary school children in England attend faith schools, predominantly Church of England and Catholic.
Dr. Campbell points out that faith schools have consistently been 'positioned and protected' by successive recent governments as a public "good": firstly, in terms of providing parents with choice and diversity; and secondly, as superior to non-faith schools in academic provision and "raising attainment."
Dr. Campbell commented, "Faith schools have been supported and championed by various politicians, across parties. Their place in the system has been defended against challenges as offering a 'public good' and being essential to 'choice and diversity.'
"But this paper highlights the selectivity of many 'faith' primary schools in under-serving children with disabilities, as well as reiterating their known under-admittance of children recorded as eligible for FSM. So it emphasizes the need to question properly the function of faith schools in contemporary England."
Dr. Campbell is Visiting Senior Fellow at the Center for Analysis of Social Exclusion (CASE) at LSE.
More information: Serving their communities? The under-admission of children with disabilities and 'special educational needs' to 'faith' primary schools in England, Oxford Review of Education (2023). DOI: 10.1080/03054985.2023.2249818
Provided by Taylor & Francis