June 15, 2023 report
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
preprint
trusted source
proofread
Old, ultra-faint and metal-poor star cluster discovered
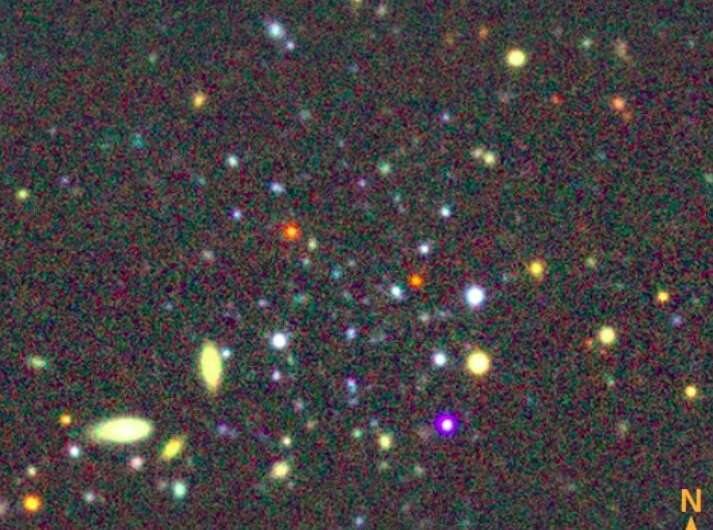

An international team of astronomers reports the discovery of a new star cluster (SC) as part of the DECam Local Volume Exploration (DELVE) survey. The newfound cluster, designated DELVE 6, is ultra-faint, metal-poor and is estimated to be about 9 billion years old. The finding was detailed in a paper published June 7 on the pre-print server arXiv.
In general, SCs are large, gravitationally bound groups of stars. They are perceived as important laboratories for studying the evolution of stars and the clusters themselves. SCs are also good tracers for exploring the structure of the Milky Way. It is estimated that the Milky Way may contain about 100,000 star clusters. The researchers suppose that many undiscovered clusters are still hidden in dense stellar regions.
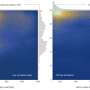
Now, a group of astronomers led by William Cerny of Yale University, has found another star cluster, not in our galaxy, but in the outskirts of the Magellanic Clouds (MCs). The detection was made through matched-filter searches over imaging from the Dark Energy Camera (DECam) processed as part of the second data release of the DECam Local Volume Exploration survey (DELVE DR2).
"In this Letter, we present the newest discovery in this ongoing census of Magellanic satellites: DELVE 6, an ancient, ultra-faint star cluster in the distant outskirts of the MCs," the astronomers wrote in the paper.
DELVE 6 (or DELVE J0212-6603) is located some 261,000 light years away from the Earth, 65,000 light years from the center of the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC), and approximately 114,000 light years from the center of the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC).
However, despite this relative proximity, DELVE 6 is located beyond the tidal radius of the LMC due to the Milky Way and the tidal radius of the SMC due to the LMC. This finding suggests that the MCs as the two possible hosts have a weak gravitational influence on DELVE 6 and that it cannot be confirmed that this system is associated with either of the Clouds.
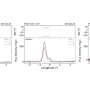
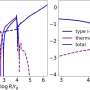
According to the study, DELVE 6 has a half-light radius of about 32.6 light years, metallicity lower than -1.17 dex, and an absolute magnitude of -1.5 mag. The cluster is estimated to be at least 9.8 billion years old. Therefore, if the association of DELVE 6 with MCs is confirmed, it may be only the second or third ancient SC associated with the SMC, or one of fewer than two dozen ancient clusters associated with the LMC.
The astronomers noted that DELVE 6 may also be a distant Milky Way halo star cluster. They added that follow-up spectroscopic observations are required in order to shed more light on the properties and origin of DELVE 6.
Summing up the results, the authors of the paper underlined that the observational census of ultra-faint systems in the MC environment is still incomplete.
"Considering the continual discovery of similar ultra-faint star cluster systems near the MCs in recent years, we speculate that a more extensive population of old, metal-poor ultra-faint star clusters may exist around the LMC, SMC, and perhaps even other low-mass galaxies in the Local Group, waiting to be uncovered by current and future surveys," the researchers concluded.
More information: W. Cerny et al, DELVE 6: An Ancient, Ultra-Faint Star Cluster on the Outskirts of the Magellanic Clouds, arXiv (2023). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2306.04690
Journal information: arXiv
© 2023 Science X Network