This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Latest research provides scientists close-up views of energetic particle jets ejected from the sun
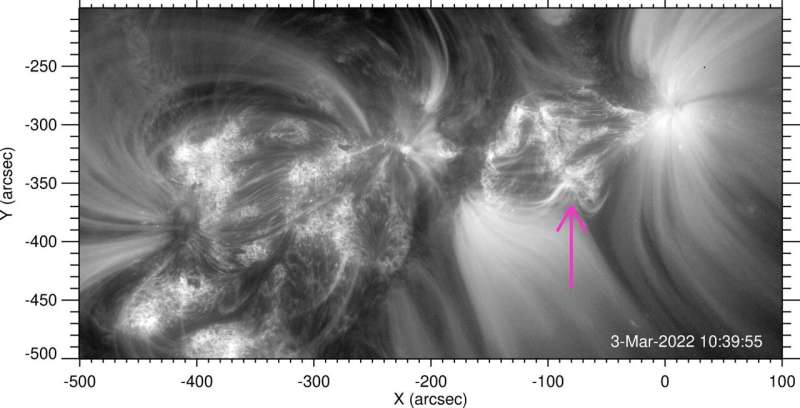
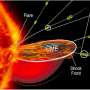
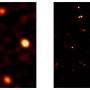
Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) scientists observed the first close-ups of a source of energetic particles expelled from the sun, viewing them from just half an astronomical unit (AU), or about 46.5 million miles. The high-resolution images of the solar event were provided by ESA's Solar Orbiter, a sun-observing satellite launched in 2020.
"In 2022, the Solar Orbiter detected six recurrent energetic ion injections. Particles emanated along the jets, a signature of magnetic reconnection involving field lines open to interplanetary space," said SwRI's Dr. Radoslav Bucik, the lead author of a new study published this month in Astronomy & Astrophysics Letters. "The Solar Orbiter frequently detects this type of activity, but this period showed very unusual elemental compositions."
In one ion injection, the intensity of the rare isotope Helium-3 exceeded the amount of hydrogen, the most abundant element on the sun, and the levels of iron were similar to the isotope Helium-4, the second most abundant element on the sun. In another injection two days later, the amount of Helium-3 had significantly decreased to an almost negligible amount.
"Our analysis shows that the elemental and spectral variations in recurrent injections are associated with the shape of the jet, the size of the jet source and the distribution of the underlying photospheric field that evolved over time," Bucik said. "We believe that understanding the variability in recurrent events from a single source sheds light on the acceleration mechanism in solar flares."
The observations made by Solar Orbiter are unique as the propagation effects that can affect abundances could be minimal near the sun. The distance of just 0.5 AU has given the scientific team a remarkably detailed view of solar events.
"When we are closer, we have a considerably better spatial resolution," Bucik said. "We are able to gain more insight into the source of these energetic particles because we can see the internal structure associated with acceleration processes as the injection evolves. Observations from twice that distance, 1 AU, are not very clear in comparison."
Bucik and his colleagues hope to learn even more from the Solar Orbiter's closest approaches to the sun at 0.3 AU.
"These observations could help predict future solar energetic particle events," Bucik said. "These particles can damage satellites and equipment and potentially harm astronauts. We want to understand how they accelerate away from the sun and what the conditions are for their acceleration."
More information: R. Bučík et al, Recurrent 3He-rich solar energetic particle injections observed by Solar Orbiter at ∼0.5 au, Astronomy & Astrophysics Letters (2023). DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202345875
Provided by Southwest Research Institute