This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Ratiometric fluorescence sensing system offers smarter and faster screening for carbendazim residues
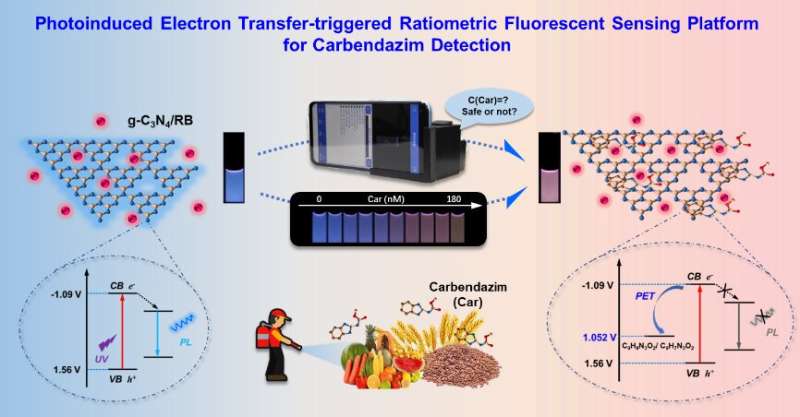
A research team led by Prof. Jiang Changlong from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has proposed a new sensing system for the detection of carbendazim residues using ultrathin graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) nanosheets and rhodamine B (RB).
Results were published in Analytical Chemistry.
Carbendazim, a common pesticide belonging to the benzimidazole family, is widely used in agricultural production. As it degrades slowly in nature, the carbendazim residues could be easily absorbed into the body through respiration, skin absorption or ingestion. At present, the common analytical methods for detecting carbendazim residues are still limited to laboratory instruments and immunoassay, etc., which entail high costs, complex operations and lengthy processing. It is of great importance to develop a new method for carbendazim detection with high sensitivity and selectivity.
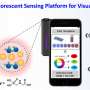
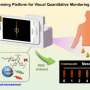
The novel photoinduced electron transfer-triggered g-C3N4Rhodamine B sensing system developed in this study was designed for selective and visual quantitative detection of carbendazim residues.
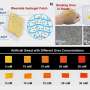
The researchers found that the carbendazim molecules could be enriched onto the g-C3N4 nanosheet by π-π stacking, then the blue-emitting fluorescence of the g-C3N4 nanosheet could be quenched by photoinduced electron transfer, while the orange fluorescence of RB remained unchanged.
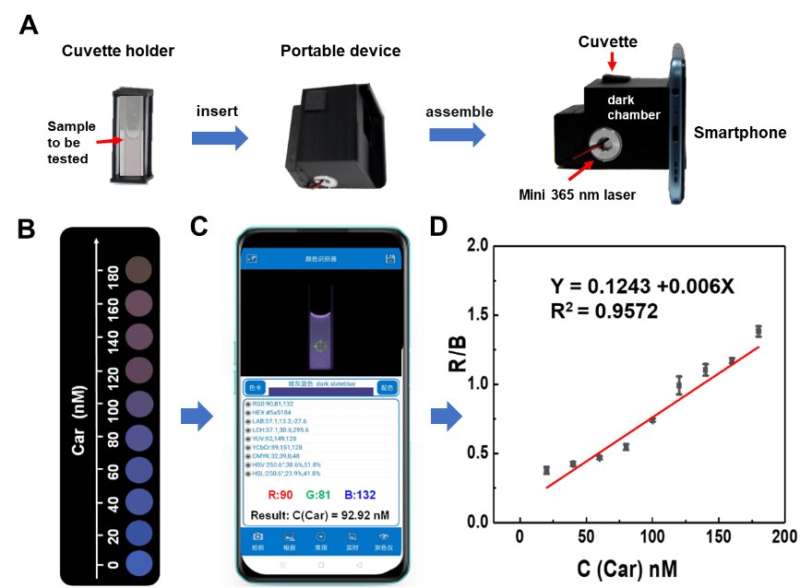
"Our sensor realized a fast visual response to trace carbendazim residues through sensitive fluorescence changes from blue to purple," said Zhang Qianru, first author of the study. The limit of detection is as low as 5.89 nM, far below the maximum residue standard.
On this basis, with the aid of 3D printing technology and color recognition, the portable intelligent sensing platform designed by the research team can be applied to the detection of carbendazim in actual samples and shows good anti-interference ability.
This study not only provides an advanced sensing strategy for sensitivity and rapid carbendazim detection in the field, but also offers new insights into other trace analytes quantitative analysis.
More information: Qianru Zhang et al, Photoinduced Electron Transfer-Triggered g-C3N4\Rhodamine B Sensing System for the Ratiometric Fluorescence Quantitation of Carbendazim, Analytical Chemistry (2023). DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.2c05691
Journal information: Analytical Chemistry
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences