International team observes innermost structure of quasar jet
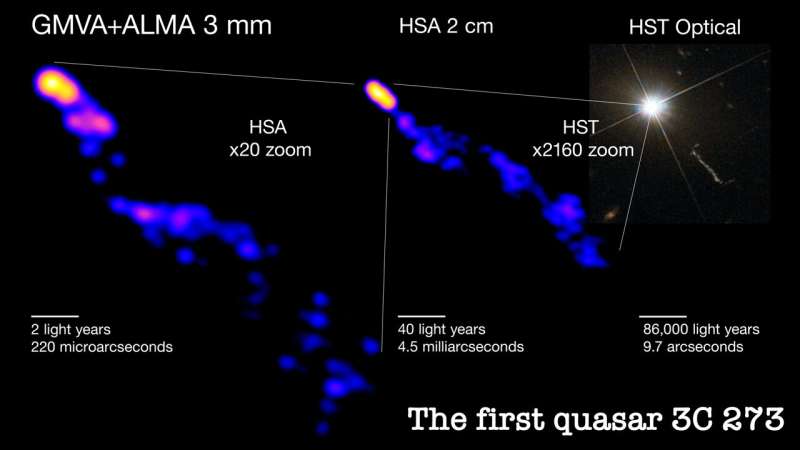
An international team of scientists has observed the narrowing of a quasar jet for the first time by using a network of radio telescopes across the world. The results suggest that the narrowing of the jet is independent of the activity level of the galaxy which launched it.
Nearly every galaxy hosts a supermassive black hole in its center. In some cases, enormous amounts of energy are released by gas falling towards the black hole, creating a phenomenon known as a quasar. Quasars emit narrow, collimated jets of material at nearly the speed of light. But how and where quasar jets are collimated has been a long-standing mystery.
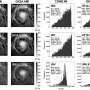
An international team led by Hiroki Okino, a graduate student at the University of Tokyo, and including members from the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ), the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Kogakuin University, Hachinohe National College of Technology, and Niigata University, captured an image with the highest angular resolution to date that shows the deepest part of the jet in a bright quasar known as 3C 273.
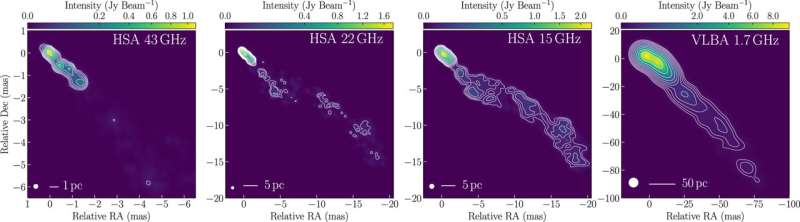
The team found that the jet flowing from the quasar narrows down over a very long distance. This narrowing part of the jet continues incredibly far, well beyond the area where the black hole's gravity dominates. The results show that the structure of the jet is similar to jets launched from nearby galaxies with a low luminosity active nucleus. This would indicate that the collimation of the jet is independent of the activity level in the host galaxy, providing an important clue to unraveling the inner workings of jets.
These results appeared in The Astrophysical Journal on November 22, 2022.
More information: Hiroki Okino et al, Collimation of the Relativistic Jet in the Quasar 3C 273, The Astrophysical Journal (2022). DOI: 10.3847/1538-4357/ac97e5
Journal information: Astrophysical Journal
Provided by National Astronomical Observatory of Japan