Amid COVID, Australians loved snitching on their neighbors

Whether it's through a sense of duty or trying to stay safe, Australians have a history of reporting wrongdoers.
We might like to pride ourselves on being a country of mateship and an almost larrikin approach to authority, but research by UNSW Law & Justice Associate Professor Catherine Bond shows Crime Stopper data skyrocketed amid the COVID-19 pandemic as we dobbed in our neighbors.
"What we see, looking at the Crime Stopper data, is that when the government creates a state of emergency, it really starts to be enthusiastically policed, including by regular people," she said.
During periods of emergency, or crisis, Australians have shown a strong tendency to report fellow citizens for indiscretions, A/Prof. Bond said.
In 2019, there were around 313,000 reports made to Crime Stoppers. In 2020, that number jumped to around 416,000. And then the figure spiked in 2021 to around 584,000.
Of those figures, in 2020, 181,000 were online reports and 235,000 were phone calls. In 2021, the number of online reports grew to 296,000 and phone call reports reached 288,000.
"This spike in the number of reports is really significant, and is just huge when you think about it," A/Prof. Bond said.
100 years of dobbing in Australia
A/Prof. Bond's research, now published in the Alternative Law Journal, draws parallels with one of Australia's last major crises—the fear of Germany during WWI.
"What we saw in WWI is in many ways the same cultural phenomenon. Australians were told, we are in a state of emergency, we are under threat. And emergency laws became quite restrictive.
"During COVID lockdowns, when working from home came into force, people also couldn't help but notice what their neighbors were up to.
"For example, there were all these new restrictions and people had a lot more time because they were working from home. They could see what their neighbors were doing much more than they usually would," A/Prof. Bond said.
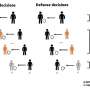
Dobbing as a sense of duty
A/Prof. Bond said that while many Australians might turn their nose up at the idea of "snitching," some dobbed people in out of a sense of duty.
"People could be taking part in this behavior because, like our ancestors in WWI, we think we're doing the right thing and are taking the moral high ground."
Associate Professor Melanie White, a sociologist in the School of Social Sciences, UNSW Arts, Design & Architecture, said our appetite for dobbing is more a question of context and our sense of loyalty at the time.
"When we perceive potential harm to our well-being or to the well-being of those close to us, the question of whether to report wrongdoing or not comes into play," A/Prof. White said.
But the decision to report others isn't without repercussions.
"Dobbing can certainly work to undermine social trust, and the social fallout for the dobber can be more consequential than any kind of institutional sanctions for the wrongdoer.
"But dobbing can be an important mechanism for social change by pushing values and norms in a new direction…if others see it as a positive contribution to the group's health," A/Prof. White said.
A/Prof. Bond said regardless of your view on whether dobbing is the right thing to do, the stats don't lie.
"Despite this supposed code of honor around not snitching, the numbers simply tell a different story," A/Prof. Bond said.
More information: Catherine Bond, Dobbing: Australia's favourite emergency pastime, Alternative Law Journal (2021). DOI: 10.1177/1037969X211062265
Provided by University of New South Wales