Ocean-surface microbes regulate climate in two new ways

Since the Industrial Revolution, the oceans have taken up about half of the anthropogenic carbon dioxide (CO2), most of which are fixed by microbial plants (plankton) into solid organic matter.
The organic matter will sink and be buried on the seabed, so that CO2 is removed from exchanging back to the atmosphere. Some of the CO2, unfortunately, remains dissolved in the ocean, making it more acid.
A review, published in Journal of Plankton Research, explained that ocean-surface microbes may be regulating the climate of the Earth in two new ways: reducing sea-atmosphere exchange and increasing foam coverage.
The researchers found that viscous and sticky organic matter secreted by microscopic planktonic plants is slowing, and thus regulating the diffusion of gases, including CO2, through the sea-air interface.
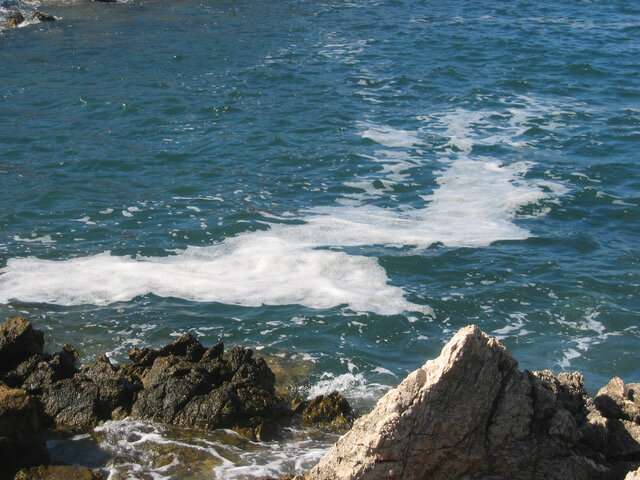
As well, it is increasing the stability of ocean foam, such as whitecaps generated when ocean waves overflow and burst. Sea foam is white, and reflects about 50 percent of incident solar light and heat back into space, while the non-foam sea surface reflects only about 5 percent. Therefore, more stable foam reduces heating of the ocean.
The International Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and other bodies are striving to better model the inputs of regulating climate change so as to reduce harmful change to the planet. This review suggests that these mechanisms need to be researched more and incorporated into climate models such as those of the IPCC.
More information: Ian R Jenkinson et al, The rôles of plankton and neuston microbial organic matter in climate regulation, Journal of Plankton Research (2021). DOI: 10.1093/plankt/fbab067
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences