Climate change, human activity threaten Libya nature reserve

A nature reserve near the capital of war-scarred Libya that has long been a sanctuary for hyenas, rare birds and plants is now under threat due to climate change and human activity.
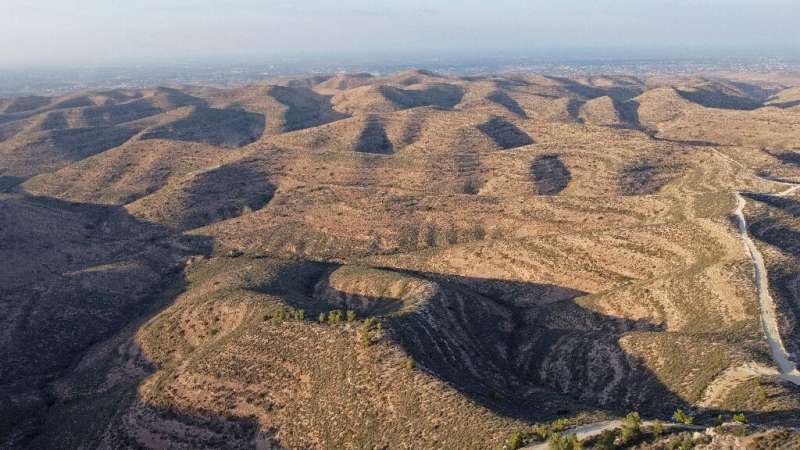
A two-hour drive east of Tripoli into the Nafusa mountain range, the Ashaafean park was added to UNESCO's list of biosphere reserves last month.
It includes dry woodland, grassland and desert on the edge of the Sahara—ideal habitats for the increasingly rare houbara bustard, a large bird.
"Ongoing climate change, the associated lack of rainfall and long waves of drought in the summer have made the reserve vulnerable to repeated fires in recent years," said Anas al-Qiyadi, of the Libyan Wildlife Trust.
Along with unauthorised logging and construction, these factors have "damaged the diversity of flora and fauna," he said.
But Qiyadi is hoping that the UNESCO listing will help protect the park.
"The biosphere reserve's 83,060-hectare (around 205,000-acre) core area is home to a variety of rare and/or endangered species," the UN cultural agency said on its website.
They include 350 plant species, some medicinal or aromatic, as well as threatened birds, reptiles and mammals.
Some 65,000 people also live in the wider park area.
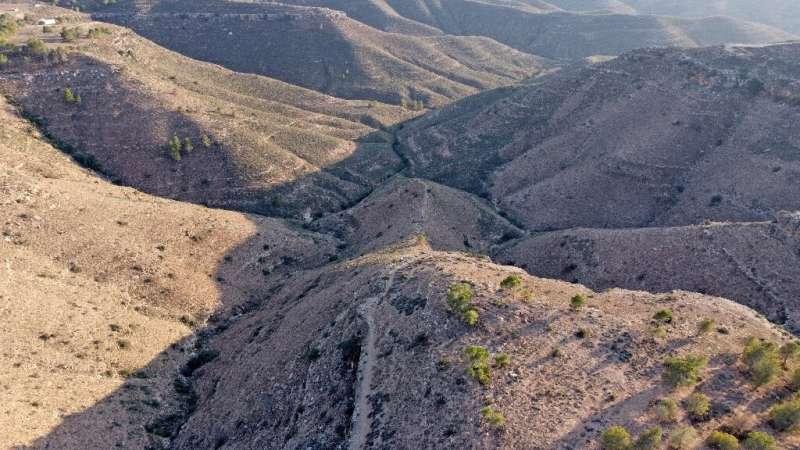

Decades of violence
Ashaafean was designated as a nature reserve under dictator Moamer Kadhafi in 1978.
But in the decade of violence that followed Kadhafi's 2011 overthrow in a NATO-backed revolt, the fragile and divided Libyan state has provided little protection to its nine nature reserves, increasingly threatened by human activity.
Qiyadi said several initiatives were underway to protect the reserves, including a programme to breed endangered tortoises in captivity and release them into the wild.
"A few days ago, we released 36 endangered tortoises into the (Ashaafean) park," he said.
Volunteers have also signed up to water trees throughout Libya's long periods of drought, Qiyadi said, adding that irrigation networks alone were not enough.
"Because the water source is a long way from the reserve, we and a group of volunteers have started campaigns to irrigate and plant more trees, but that needs ongoing attention."
'International attention'
Drought and deadly forest fires hit several countries across the Mediterranean this year, notably in neighbouring Algeria.
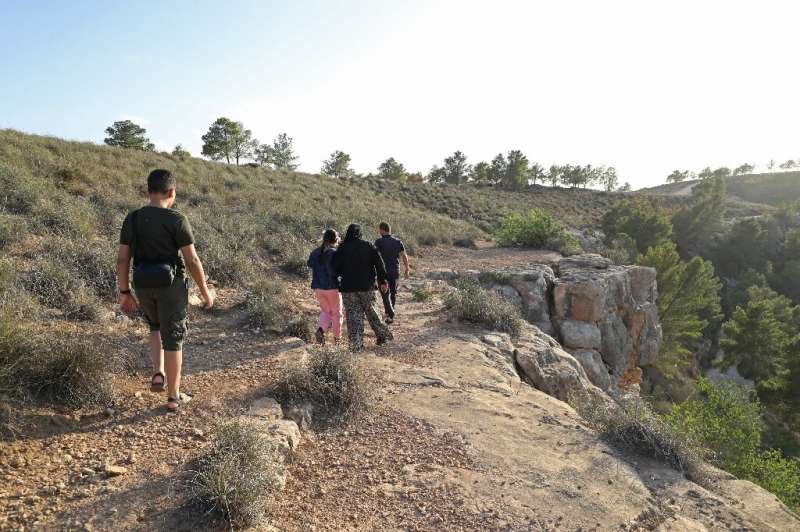

Libya was largely spared this time, but since 2015 it has seen huge fires that have killed many endangered animals and trees over a century old.
Ashaafean is the first Libyan site to be categorised as a UNESCO biosphere reserve.
The designation aims to promote sustainable development, protect ecosystems and help support research and education.
Tareq al-Jdeidy, a scientist at the University of Tripoli who led a campaign for the listing, said it was a step towards better protection for one of Libya's most precious reserves.
The designation means "it will attract attention internationally from organisations focusing on the environment, plant and animal life—there will be studies on how to develop it," he said.
According to UNESCO, most of the reserve's residents make a living from traditional sustainable agriculture as well as wood gathering and beekeeping.
"The region is known for the quality of its olives and oil," it said when announcing the designation.
Jdeidy hopes the park will both help the local economy and serve as an example of efforts to combat desertification.
"It will support local residents both directly and indirectly through development programmes linked to the reserve," he said.
© 2021 AFP