Mushballs stash away missing ammonia on Uranus and Neptune
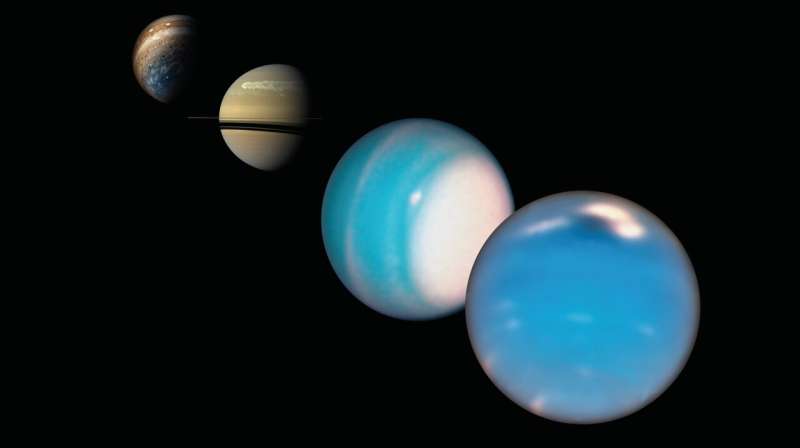

Mushballs—giant, slushy hailstones made from a mixture of ammonia and water—may be responsible for an atmospheric anomaly on Neptune and Uranus that has been puzzling scientists. A study presented by Tristan Guillot at the Europlanet Science Congress (EPSC) 2021 shows that mushballs could be highly effective at carrying ammonia deep into the ice giants' atmospheres, hiding the gas from detection beneath opaque clouds.
Recently, remote observations at infrared and radio wavelengths have shown that Uranus and Neptune lack ammonia in their atmosphere compared to the other giant planets in our solar system. This is surprising because they are otherwise very rich in other compounds, such as methane, found in the primordial cloud from which the planets formed.
Either the planets formed under special conditions, from material that was also poor in ammonia, or some ongoing process must be responsible. Guillot, a researcher at the CNRS, Laboratoire Lagrange in Nice, France, turned to a recent discovery at Jupiter for a possible answer to the puzzle.
"The Juno spacecraft has shown that in Jupiter, ammonia is present in abundance, but generally much deeper than expected—thanks to the formation of mushballs. I show that what we have learned at Jupiter can be applied to provide a plausible solution to this mystery at Uranus and Neptune," said Guillot.
The Juno observations at Jupiter have shown that ammonia-water hailstones can form rapidly during storms because of ammonia's ability to liquefy water ice crystals, even at very low temperatures of around -90 degrees Celsius. Models indicate that these mushballs in Jupiter may grow to weights of up to a kilogram or more, slightly higher than the largest hailstones on Earth. As they plunge downwards, they transport ammonia very efficiently to the deep atmosphere, where it ends up locked away beneath the cloud base.
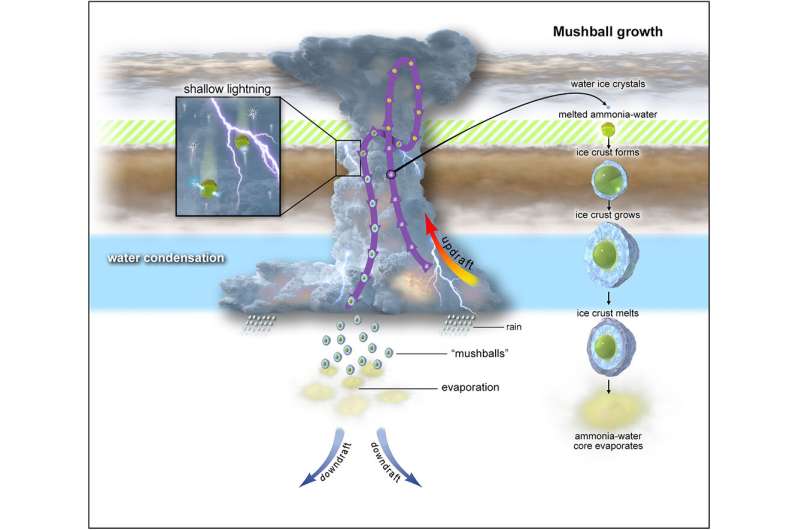
"Thermodynamic chemistry implies that this process is even more efficient in Uranus and Neptune, and the mushball seed region is extended and occurs at greater depths," said Guillot. "Thus, ammonia is probably simply hidden in the deep atmospheres of these planets, beyond the reach of present-day instruments."
To determine exactly how deep down the mushballs are carrying ammonia and water may have to wait until an orbiter with instruments can probe the atmospheres of the ice giants close up.
"To fully understand the processes, we need a dedicated mission to map the deep atmospheric structure and understand mixing in hydrogen atmospheres," said Guillot. "Neptune and Uranus are a critical link between giant planets, like Jupiter and Saturn, and ice giant exoplanets that we are discovering in the galaxy. We really need to go there."
More information: Tristan Guillot, Mushballs and the lack of Ammonia in Uranus and Neptune, (2021). DOI: 10.5194/epsc2021-422
Provided by Europlanet