Permafrost degradation affects hydrological factors in source area of Yellow River

Climate warming has accelerated the permafrost degradation, which influences the processes of water supply, runoff and discharge in the Source Area of the Yellow River (SAYR) in the northeast of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.
Permafrost interacts with surface water and groundwater. In particular, topography, active faults and permafrost degradation control the distribution of groundwater.
Recently, a research team led by Prof. Sheng Yu from Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources (NIEER) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) investigated the process of permafrost degradation and the response of its key hydrological factors in the SAYR driven by climate change.
The study was published in Hydrological Sciences Journal.
The researchers simulated the change process of four types of permafrost by combining with the heat conduction calculation model. Based on GIS spatial analysis, the temporal and spatial changes of permafrost in the SAYR in the past 50 years and the next 100 years were also presented.
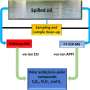
In addition, they also compared the differences of hydrological factors under different degraded states of frozen soil based on the field monitoring and indoor simulation.
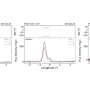
"The soil water content in the permafrost area gradually increases to reach a saturated state with the thawing of soil. Influenced by the barrier of the permafrost layer, the interflow accumulates near the permafrost table," said Prof. Sheng. "It leads to significant increase of suprapermafrost water level in the permafrost area."
Additionally, the hydrological process of permafrost was also affected by local factors such as rainfall evaporation, soil texture, terrain, vegetation cover and hydrogeological conditions.
The study provides scientific basis for further understanding of the formation process and evolution law of runoff in the Yellow River Basin, as well as theoretical support for accurately predicting the ecological and hydrological effects of permafrost changes in SAYR.
More information: Wei Cao et al, Differential response to rainfall of soil moisture infiltration in permafrost and seasonally frozen ground in Kangqiong small basin on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, Hydrological Sciences Journal (2021). DOI: 10.1080/02626667.2021.1883619
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences