Plant diversity in Yunnan: Current status and future directions
Yunnan, located in the southwest border of China, has a complex natural environment and breeds extremely rich biological resources. It is known as the "Kingdom of Animals and Plants."
It is one of the 17 biodiversity hot spots in China and one of the 34 biodiversity hot spots in the world. Although the land area only accounts for 4.1% of China, it nearly harbors half of the total number of higher plant species of China (about 19,000 species), which has always attracted the attention of researchers all over the world.
The research groups for Plant Diversity and Evolution of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and Himalayas from the Kunming Institute of Botany has been continuously focused plant diversity of Yunnan. Based on the available data from latest released publications and online resources, the researchers analyzed the current situation of plant diversity in Yunnan Province.
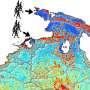
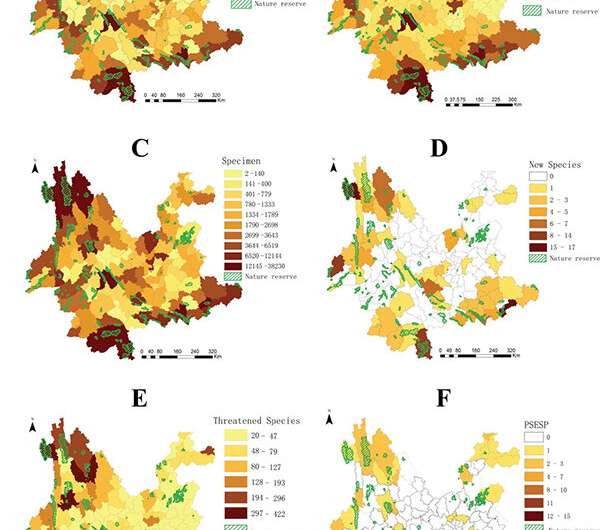
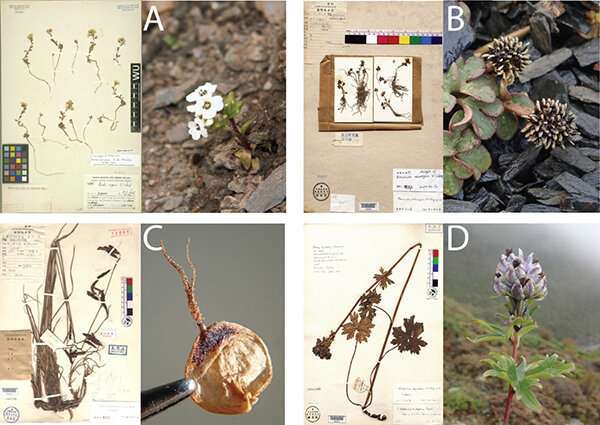
They found that the northwest, south and southeast of Yunnan are the areas with the largest number of species, endemic species, specimens collected, new species published in recent seven years and endangered species, while the southeast of Yunnan are the hot spot of plant species with extreme small population.
In addition, combined with the data of nature reserve, result showed that although there are currently 160 protected areas in Yunnan, only 109 of the 129 county-level administrative units have protected areas.

Moreover, the protected areas in the central and eastern Yunnan are low grade (County and Municipal Level), with small area and relatively fragmented distribution, which may be related to the frequent human activities in central and eastern Yunnan
On this basis, in order to better protect biodiversity resources and achieve sustainable development in the future, the researchers put forward many suggestions for the future development of plant diversity in Yunnan, such as: government support is needed for scientific research, the need to investigate the plant resources of Yunnan (especially in the weakly investigated area), and support the qualified monographs, flora and the other biodiversity databases.
The related studies, titled "Plant diversity in Yunnan: Current status and future directions," were recently published in Plant Diversity's special issue "Safeguarding Our Future by Protecting Biodiversity."
More information: Li-Shen Qian et al. Plant diversity in Yunnan: Current status and future directions, Plant Diversity (2020). DOI: 10.1016/j.pld.2020.07.006
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences