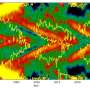
Agricultural fires in central Africa light up in Suomi NPP satellite image
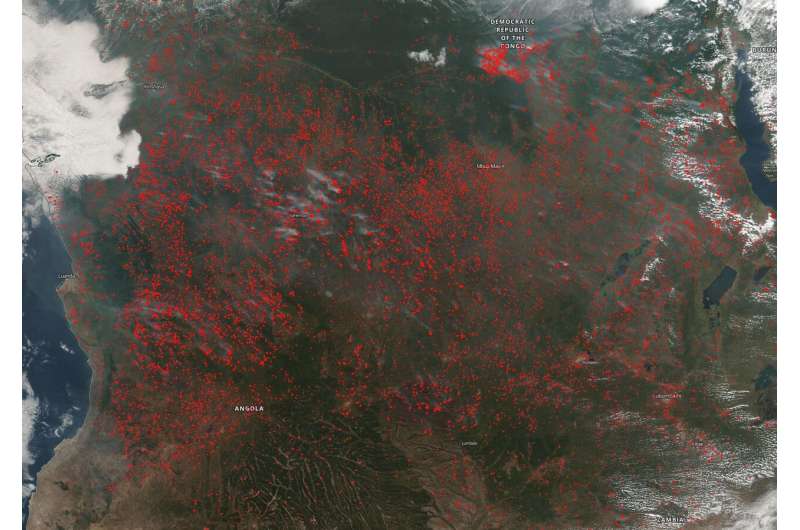
Fires have spread across the majority of the landscape in Angola and the Democratic Republic of the Congo in this NOAA/NASA Suomi NPP satellite image using the VIIRS (Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite) instrument from June 25, 2020. Fires of this number are not uncommon at this time of year in Africa. During the agricultural season of clearing field and planting new ones, farmers set fire to the remains of old crop fields to rid them of the leftover grasses and scrub. This action also helps return nutrients to the soil to ensure a good crop during the next planting season.
This agricultural ritual is one that is at least 12,000 years ago. It is economical for the farmer since large equipment is not needed to clear the fields. In Angola, the Global Forest Watch website (using data from the VIIRS instrument on the Suomi NPP satellite) had 61,661 alerts for fires for the past week (June 18—June 25). In the Democratic Republic of the Congo there are 102,738 VIIRS alerts for fire for that same period.
"Slash and burn" agriculture is practiced most often in regions including parts of Africa, northern South America, and Southeast Asia, where an abundance of grasslands and rainforests are found. While fire helps enhance crops and grasses for pasture, the fires also produce smoke that degrades air quality. The smoke released by any type of fire (forest, brush, crop, structure, tires, waste or wood burning) is a mixture of particles and chemicals produced by incomplete burning of carbon-containing materials. All smoke contains carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide and particulate matter or soot and is hazardous to breathe.
Provided by NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center