August 27, 2019 report
WISE J0720−0846 hosts a massive T dwarf, observations confirm

By combining high-precision astrometry and adaptive optics-resolved imaging, astronomers have found that the binary system WISE J0720−0846, better known as Scholz's star, hosts a T dwarf, confirming previous assumptions. The finding is reported in a paper published August 19 on arXiv.org.
Brown dwarfs are intermediate objects between planets and stars. Astronomers generally agree that they are substellar objects occupying the mass range between 13 and 80 Jupiter masses. One subclass of brown dwarfs (with effective temperatures between 500 and 1500K) is known as T dwarfs, and represents the coolest and least luminous substellar objects so far detected.
Studies of T dwarfs could help astronomers better understand objects near the disputed planet/star boundary, for instance, giant exoplanets. However, although many brown dwarf have been detected to date, T dwarfs are not so common, as only about 400 such objects have been identified.
Now, a team of astronomers led by Trent J. Dupuy of Gemini Observatory, reports the finding of another T dwarf. Using the Keck II telescope and the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope (CFHT), they confirmed that Scholz's star hosts a T dwarf companion.
Located some 22 light years away, Scholz's star (WISE J072003.20−084651.2 or WISE J0720−0846), is a binary system with a red dwarf primary star. The binary is known for its fly-by of the solar system that took place about 70,000 years ago, when it passed by the sun at a distance of some 52,000 AU. In 2015, researchers suggested that the system harbors a T-dwarf companion, and new observations made by Dupuy's team now provide evidence confirming this assumption.
"As part of our ongoing effort to measure dynamical masses for ultracool dwarfs, we have monitored WISE J0720−0846 with Keck AO [adaptive optics] and CFHT wide-field astrometry for the past several years," the astronomers wrote in the paper.
The monitoring campaign yielded essential information regarding the fundamental parameters of Scholz's star. Most importantly, the observations delivered precise individual dynamical masses and an improved distance measurement.
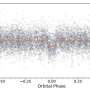
In particular, the study found that the system is located approximately 22.17 light years away, and has a moderately eccentric orbit with an eccentricity of about 0.24 and period of around 8.06 years. The two components are separated from each other by 2.17 AU.
The dynamical masses of the primary star and its companion were estimated to be about 99 and 66 Jupiter masses, respectively. The effective temperature of the less massive object was calculated to be around 1250K.
The results indicated that the brown dwarf is, indeed, a T dwarf several billion years old, rather massive when compared to other similar objects of this type.
"The relatively high mass of the cold (Teff = 1250±40 K) brown dwarf companion indicates an age older than a few Gyr, in accord with age estimates for the primary star, and is consistent with our recent estimate of ≈ 70 Mjup for the stellar/substellar boundary among the field population," the researchers noted.
Moreover, the results allowed the scientists to estimate the parameters of the binary's recent close encounter with the solar system. According to the study, Scholz's star passed within 68,700 AU of the sun about 80,500 years ago.
More information: T. Dupuy, et al. WISE J072003.20-084651.2B Is A Massive T Dwarf. arXiv:1908.06994v1 [astro-ph.SR]: arxiv.org/abs/1908.06994
© 2019 Science X Network