Precision calibration empowers largest solar telescope
An article published in the SPIE publication Journal of Astronomical Telescopes, Instruments, and Systems (JATIS), "Polarization Modeling and Predictions for DKIST Part 5: Impacts of enhanced mirror and dichroic coatings on system polarization calibration," marks a substantial advance in ensuring the accurate solar information measured and collected by the Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope (DKIST).
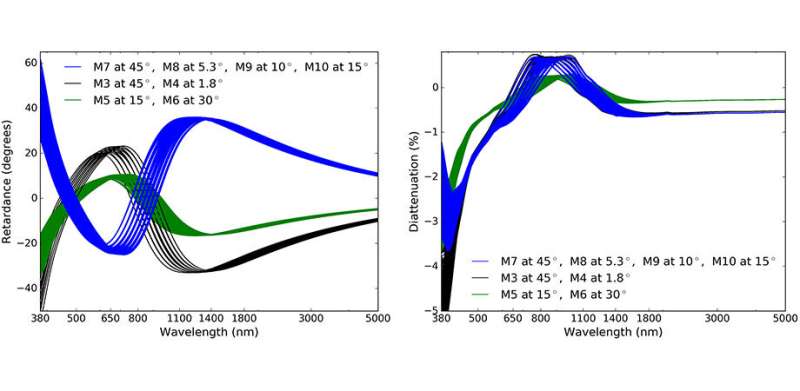
As with any astronomical instrument, calibration is required in order to remove effects that the instrument itself might have on the data. By concentrating on characterizing the telescope's thin film metal coatings, anti-reflection coatings, and dichroic mirrors, the authors have developed unique computer models based on laboratory data for the polarization transmissivity of the entire telescope system.
Not only was the team able to predict the performance of a variety of devices in the optical system, they were also able to specify, design, and build compensating devices to correct for unwanted polarization. In addition, the team has the ability to fit multi-layer coating designs; this allows them to predict system-level polarization properties of mirrors, anti-reflection coatings, and dichroics at arbitrary incidence angles, high spectral resolving power, and on curved surfaces through optical modeling software packages. Altogether, the researchers have demonstrated confidence in the precision calibration of the telescope.
According to JATIS Associate Editor and SPIE Fellow James Breckinridge, the findings will help ensure that the DKIST will be one of science's most powerful observational instruments: "In order to make sure you're measuring what's going on in the sun and not in the instruments, you have to calibrate the instrumentation, which is precisely what this research has successfully demonstrated. I believe that this telescope system has the most accurate and comprehensive polarization calibration of any astronomical telescope in the world. This will allow astronomers to measure solar features and activity to unprecedented accuracy, and should lead to many significant discoveries."
More information: David M. Harrington, Polarization modeling and predictions for Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope part 5: impacts of enhanced mirror and dichroic coatings on system polarization calibration, Journal of Astronomical Telescopes, Instruments, and Systems (2019). DOI: 10.1117/1.JATIS.5.3.038001
Provided by SPIE