Research advances smartphone solution for diagnostic testing in remote rural areas

A Simon Fraser University researcher is hoping to help women in rural areas access information about their reproductive health using a common tool in their pockets: a smartphone.
Zhendong Cao has developed a unique way to take advantage of a smartphone's camera so that it could eventually help perform non-clinical diagnostic testing, with initial applications that can help women with family planning and reproductive health monitoring.
Cao's thesis project was co-supervised by engineering science professor Ash Parameswaran and health sciences professor Pablo Nepomnaschy. The research addresses a key challenge for Nepomnaschy's field studies in Guatemala.
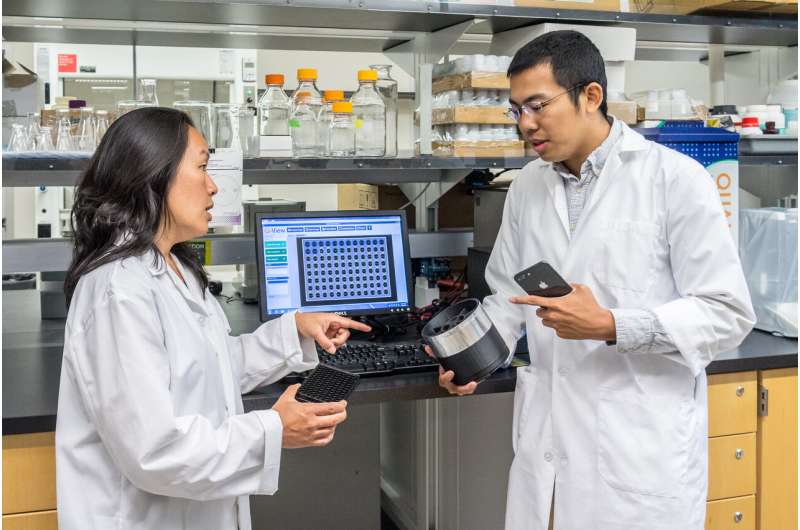
"A smartphone's camera can distinguish up to 16-million colours," says Cao, who recently graduated with a master's degree in applied sciences. "We're taking advantage of this capability to do the same kind of diagnostic testing that a microplate reader does in a laboratory—except we're using an everyday phone."
Typically, researchers perform diagnostic tests in a laboratory that is equipped with a microplate reader. Microplate readers can cost thousands of dollars and weigh more than 50 pounds. Cao's device is part of a system that, when completed, will allow researchers to carry out those same laboratory tests anywhere in the world.
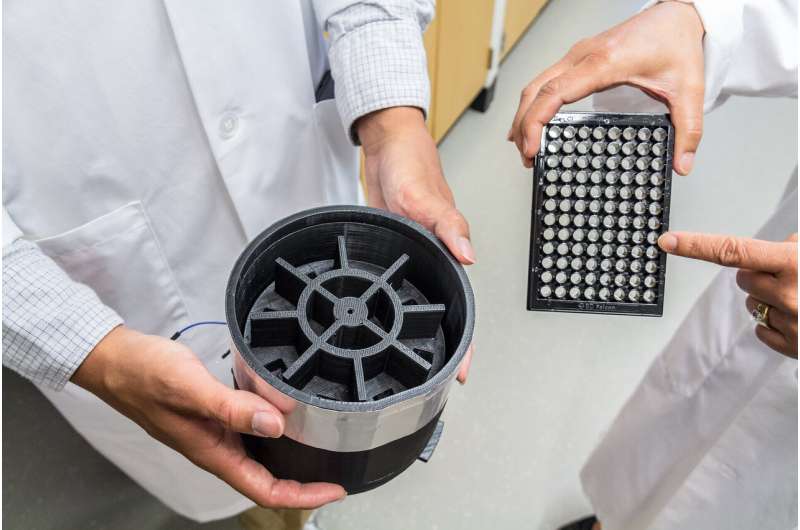
To develop his technology, Cao modified the software inside a smartphone's camera to analyze the amount of coloured pixels and UV light in a photo of a biological sample.
The colours in the photo's pixels correspond to a known "signature" produced by a substance—for example, estrogen—that the researcher or health-care provider is investigating. The way light is absorbed or emitted can indicate a sample's concentration, such as how much estrogen is present in saliva. In addition to estrogen, the researcher or clinician could test other indicators of women's reproductive health and stress levels, which could affect her ability to get pregnant.
To improve the accuracy and efficiency of the tests, Cao also created a light-blocking container the size of a cookie tin that houses multiple samples for testing. The container shields against interference from ambient light and helps the smartphone capture a more precise image. Altogether, Cao demonstrated that the result of the smartphone's tests were comparable to the original microplate reader technology.
Cao's innovation could enable high-quality lab testing to become hand-held, supporting faster research in the short term, or perhaps one day, more rapid access to reproductive health information and diagnoses in rural areas.
"When we're collecting samples for our research with women in these rural areas, we ship our samples back to our lab to analyze them," explains Katrina Salvante, a research associate in Nepomnaschy's lab who collaborated on Cao's project. "We're hoping to replace the expensive and bulky equipment we use in our lab with a smartphone, which researchers like us could carry out to the field and that the women themselves could access, too."
If commercialized, health-care workers could use the results provided by the smartphone testing kit to inform female patients about their daily reproductive status in real time so they can make decisions about family planning and overall reproductive health.
Furthermore, Cao's innovation could have wide-ranging applications in the long term.
"We started with the question about fertility testing with Pablo's lab," says Parameswaran. "But this could have all sorts of applications. We're already thinking about its potential for cancer detection, food safety, or even livestock health.
"We want to create technologies that are accessible, cheap and can improve access to quality science no matter where someone is located."
"It's exciting to work on technologies that have important potential," says Cao, who is working on a project to develop wireless health information monitoring for hospitals as a research assistant in Parameswaran's lab this summer. "I'm proud to be part of—and contribute to—socially and technologically important projects."
Provided by Simon Fraser University