The shape of a perfect storm: Saving lives by predicting firestorms
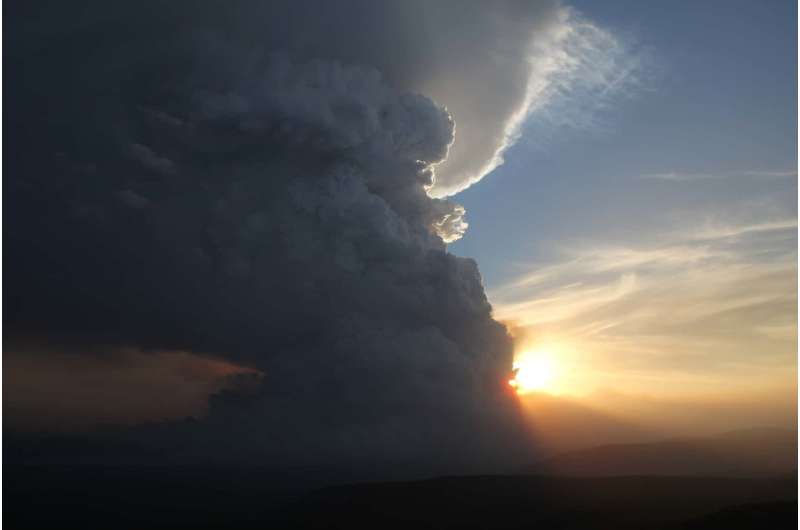

Firestorms are a nightmare for emergency services and anyone in their path. They occur when a bushfire meets a 'perfect storm' of environmental conditions and creates a thunderstorm.
Dr. Rachel Badlan and Associate Professor Jason Sharples are part of a team of experts from UNSW Canberra and ACT Emergency Services that has found the shape of a fire is an important factor in whether it will turn into a firestorm.
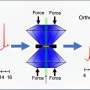
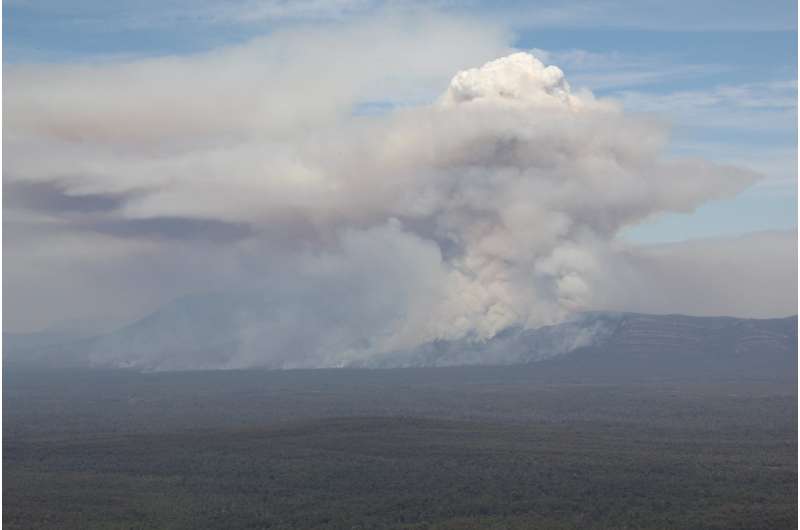
Fires that form expansive areas of active flame, rather than spreading as a relatively thin fire-front, are more likely to produce higher smoke plumes and turn into firestorms, the researchers found.
This finding is being used to underpin further development of a predictive model for firestorms. The model was trialed in the 2015 and 2016 fire seasons by the ACT Emergency Services Agency and the NSW Rural Fire Service, and now forms part of the national dialogue around extreme bushfire development.
The model will help identify the most dangerous fires and better determine the best deployment of fire resources, saving more lives and restricting the damage when firestorms strike.
"Thunderstorms generated by the heat from a fire are the most dangerous manifestation of a bushfire. These firestorms create their own weather with lightning, strong winds, and even tornadoes that spread fire in multiple directions. These ingredients make them impossible for firefighters to put out," says Rachel, who is a postdoctoral fellow at UNSW Canberra.
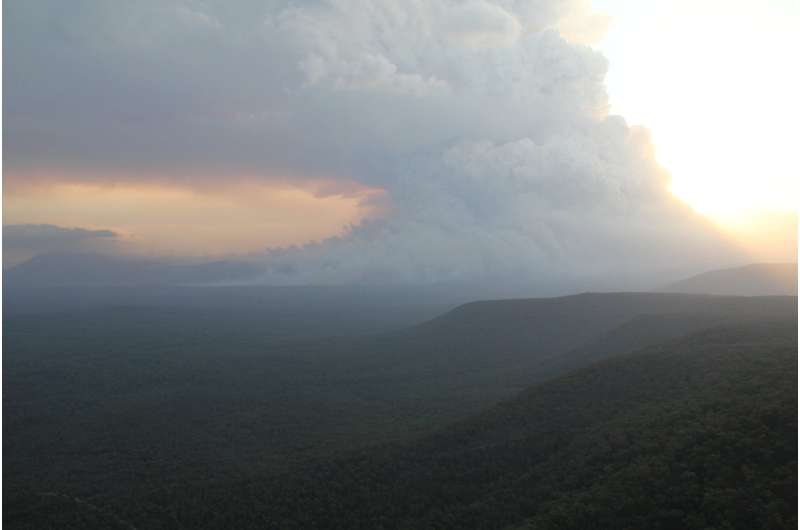

"Before this model, there was no way to predict which fires would become firestorms. Previous work attributes these firestorms solely to the total energy released by the fire, however, we have found the shape of a fire is a vital factor in the development of firestorms," Rachel says.
The team used advanced computer models to incorporate details of the environment (terrain, wind, and atmosphere) and the fire's shape, size and intensity, to determine how high the plume will be.
This information then tells the researchers about the potential for a fire to develop into a firestorm (known as a pyrocumulonimbus).
"With firestorms commonly occurring in Australia—more than 50 since 2001—and set to increase due to hotter and drier conditions, it's vital that fire managers can determine which fires are likely to transition into a firestorm so that evacuation may occur as early as possible," Rachel says.

More information: Conference paper: The role of deep flaming in violent pyroconvection. www.researchgate.net/publicati … olent_pyroconvection
Provided by Freshscience