Scientists successfully print glass optics
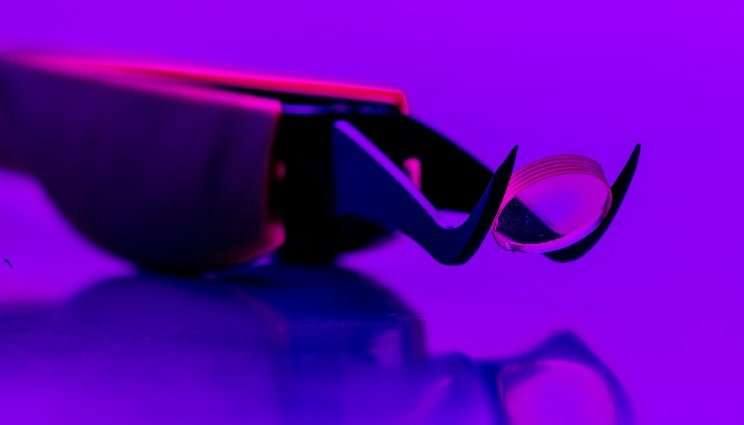

For the first time, researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) have successfully 3-D-printed optical-quality glasses, on par with commercial glass products currently available on the market.
In a study published in the journal Advanced Materials Technologies, LLNL scientists and engineers describe successfully printing small test pieces from Lab-developed ink with properties "within range of commercial optical grade glasses."
Because the refractive index of glass is sensitive to its thermal history, it can be difficult to ensure that glass printed from the molten phase will result in the desired optical performance, researchers said. Depositing the LLNL-developed material in paste form and then heating the entire print to form the glass allows for a uniform refractive index, eliminating optical distortion that would degrade the optic's function.
"Components printed from molten glass often show texture from the 3-D-printing process, and even if you were to polish the surface, you would still see evidence of the printing process within the bulk material," said LLNL chemical engineer Rebecca Dylla-Spears, the project's principal investigator. "This approach allows us to obtain the index homogeneity that is needed for optics. Now we can take these components and do something interesting."
The custom inks, aimed at forming silica and silica-titania glasses, allow researchers the ability to tune the glass's optical, thermal and mechanical properties, Dylla-Spears said. For the study, researchers printed small, simple-shaped optics as proof of concept, but Dylla-Spears said the technique eventually could be applied to any device that uses glass optics and could result in optics made with geometric structures and with compositional changes that were previously unattainable by conventional manufacturing methods. For example, gradient refractive index lenses could be polished flat, replacing more expensive polishing techniques used for traditional curved lenses.
"Additive manufacturing gives us a new degree of freedom to combine optical materials in ways we could not do before," Dylla-Spears said. "It opens up a new design space that hasn't existed in the past, allowing for design of both the optic shape and the optical properties within the material."
More information: Joel F. Destino et al. 3D Printed Optical Quality Silica and Silica-Titania Glasses from Sol-Gel Feedstocks, Advanced Materials Technologies (2018). DOI: 10.1002/admt.201700323
Provided by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory