Scientists work to lift the mystery of persistent haze
Outdoor air pollution, under certain atmospheric conditions, can result in a dark, dangerous haze. It causes sickness, halts flights, and closes highways. And it's happening more often, according to the cover article of the latest issue (No. 4) of Advances in Atmospheric Sciences .
"The increasing tendency and severity of persistent haze events can be the results of more pollution and worse weather," said Yihui Ding, a senior scientist at the National Climate Center in Beijing, China, and an author on the paper. He noted that the increasing number of "haze days" continues to cause serious harm to human health.
While individual haze events have been described and studied previously, this is the first study to comprehensively investigate the events and the atmospheric conditions surrounding them. The researchers aimed to understand how weather effects, such as high humidity and weak surface wind, influence haze formation.
"Understanding the mechanisms can provide an important precursor or signature for the later sudden outbreak of severe and persistent haze events, which set a stage for complex chemical and biological reactions and interactions leading to more persistent haze events," said Ding.
In their study, the researchers used standardized factors to objectively identify haze events in China's national capital region of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei from 1980 through 2013. They analyzed the atmospheric conditions of the identified events, and explored the air-motion mechanism by which haze events formed and persisted.
The researchers identified 49 persistent haze events, each lasting for at least three days with limited visibility. Seven of the events occurred in the 1980s, lasting a total of 23 days. The 1990s saw nine events, lasting a total of 33 days. The number of events and total days nearly doubled in the first decade of this century, with 17 events totally 60 days. The first three years of the current decade have included 16 events, with a total of 77 days spent in haze.
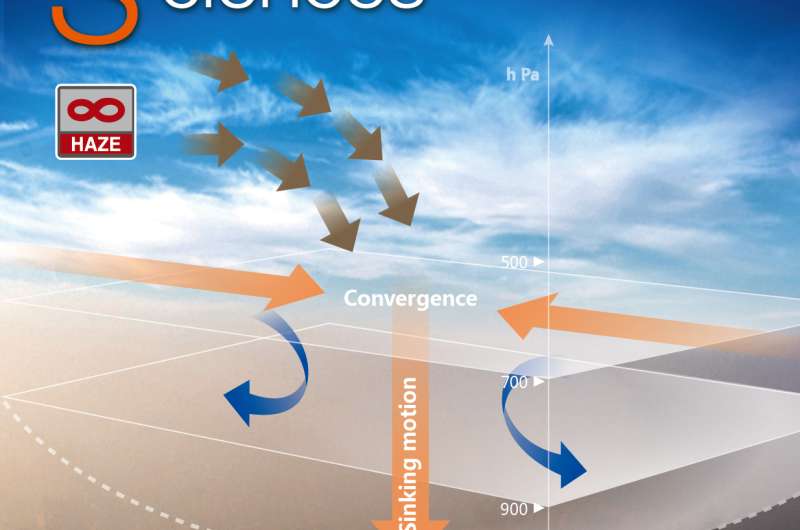
The scientists also found that the haze events had one of two specific circulation patterns, both of which can produce a strong sinking motion in the atmosphere. The air, thick with pollutants, stays trapped close to the Earth until the atmospheric conditions shift and the pressure lifts.
Now that the scientists are beginning to better understand how the hazes form, the next step is to improve the predictability of such events.
"We are going to develop the predictive technique of dynamic and circulation conditions, as well as the influence on the structures of the boundary layer at weekly and monthly scales," Ding said.
More information: Ping Wu et al, Atmospheric circulation and dynamic mechanism for persistent haze events in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region, Advances in Atmospheric Sciences (2017). DOI: 10.1007/s00376-016-6158-z
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences