Food webs in brown water lakes are more resilient to nitrogen deposition

Nitrogen deposition caused by human activities can lead to an increased phytoplankton production in boreal lakes. The response of boreal lakes to nitrogen deposition will strongly depend on each lake's content of organic carbon, which are predicted to increase with future warmer and wetter climate. This according to a thesis at Umeå University.
The worldwide increase of inorganic nitrogen deposition via fossil fuel combustion, fertilization and forestry has been intervening drastically with the Earths' natural nitrogen cycle. Food webs of boreal lakes, that have historically received little nitrogen deposition until now, are expected to be especially susceptible to increases in inorganic nitrogen availability.
Simultaneously, global change mediated by warming, increased precipitation, and reduced atmospheric sulfate deposition is enhancing terrestrial dissolved organic carbon loadings to aquatic systems.
However, whole lake experiments demonstrating the consequences of increased inorganic nitrogen and organic carbon availability on productivity and food web structure in natural boreal lakes have been missing until now.
To address these questions, Anne Deininger conducted whole lake nitrogen fertilization experiments. She studied six lakes in Northern Sweden with naturally different organic carbon concentrations (two clear lakes, two lakes with intermediate levels of organic carbon, and two organic carbon rich lakes, "brown") over three years.
The set-up included one year measuring reference conditions and two years with experimental nitrogen manipulations. Then, Anne Deininger followed how the added nitrogen entered the food chain, how it affected different organisms groups, and lastly tested whether the response differed depending on the lakes organic carbon contents.
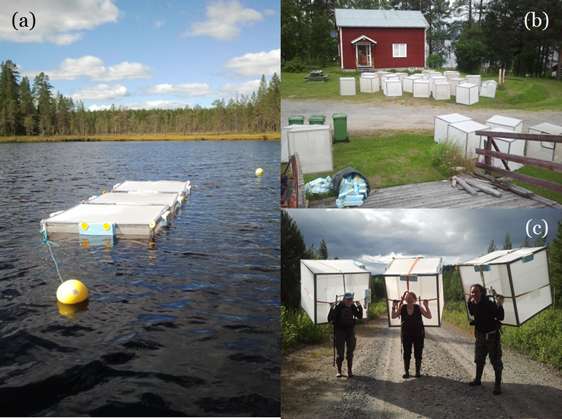

Nitrate addition clearly enhanced phytoplankton production and biomass in all experimental lakes. However, Anne Deininger found that this stimulating nitrogen effect decreased with increased lake organic carbon content caused by the attributed light reduction.
"This is very interesting results because it shows that the response of boreal lake food webs to enhanced nitrogen deposition is strongly linked to the organic carbon concentration within each lake. In turn, it also means that global change and its effects on the global carbon cycle will strongly determine the response of boreal lakes to changes in nitrogen deposition. This is something we could only speculate upon until now," says Anne Deininger.
Another important question addressed in the thesis is how nitrogen deposition might affect phytoplankton consumers, and the food web structure in general. Interestingly, also the response of consumers (i.e. zooplankton) to nitrogen addition differed depending on the organic carbon content of each lake. Especially in clearer lakes with low organic carbon content, phytoplankton became so enriched in nitrogen that they became poor quality food items for zooplankton. Thus, although food resources increased with nitrogen addition, its decreased food quality resulted in reduced growth of their consumers and less energy being transferred up the food chain. In browner and more organic carbon rich lakes, food quality was not reduced to the same extent as in clear water lakes and the food web was clearly more resilient to nitrogen addition.
"In summary, my thesis suggests that any change in the landscape that enhances inorganic nitrogen availability will especially affect food webs in the open water zone of clear water lakes. In contrast, global change induced increase in organic carbon export from land to boreal lakes will result in more lakes with lower phytoplankton production and biomass and with food webs being more resilient to enhanced nitrogen deposition," says Anne Deininger.
Importantly, as a next step future research needs to resolve where the nitrogen deposited to organic rich lakes eventually ends up. Since it is not taken up so efficiently by the food web in the open water zone, it might enter microbial pathways is the lake bottom directly or alternatively be washed out and taken up by downstream stream bank vegetation.
In times of increasing computer capacities, gathering empirical field experiments data is crucial to build predictive frameworks and models to diagnose when, where and how ecosystems will respond to global change and changes in nitrogen deposition.
"This was part of my work and developing such models is important, as it will greatly aid our ability to manage future global change."
More information: "Effects of inorganic nitrogen and organic carbon on pelagic food webs in boreal lakes." www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/ … 66248/FULLTEXT01.pdf
Provided by Umea University